Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: What Sets Them Apart
Edge computing and cloud computing are among the technologies that are really shaping how data is being processed and managed today. The key difference would be edge computing, which processes data closer to its source, whereas cloud computing does this via large centralized data centers, perhaps located pretty far from the sources. This difference may significantly impact performance, speed, and efficiency.
These are the conditions under which the terms below matter for businesses and individuals with more devices connected to the internet. Edge computing can provide quicker responses to real-time applications; on the other hand, cloud computing offers heavy storage and strong processing for bigger datasets.
The concept of both will be discussed in this post, and by the end of it, readers will know which solution might best fit the needs.
Key Takeaways
Edge computing provides faster data processing by doing so nearer to the source.
Cloud computing provides huge storage and processing capabilities through remotely accessed servers.
Both technologies stand vitally important in this data-driven world today.
Basics of Edge Computing
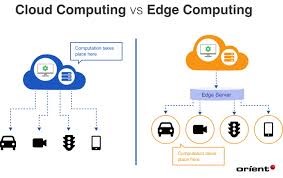
Edge computing is the technique for arranging a network that brings computation and storage closer to devices generating the data. This approach reduces latency and bandwidth use, improving efficiency for real-time applications.
Definition and Core Concepts
Edge computing is a computing architecture that allows for processing data at the edge of the network, rather than depending on some central data center. Data is analyzed near its source, from the IoT device to local servers.
It comprises the following critical elements:
- Edge Devices: These are the physical devices that gather data, like sensors and cameras.
- Edge Nodes: Devices that process data and offer cloud connectivity.
- Data Processing: This happens at a very fast rate to support real-time decisions. This architecture will ensure better performance by shortening the distance that data has to travel, hence avoiding delays and increasing response time.
Major Benefits and Applications
Edge computing offers a number of the following primary benefits, which make it very beneficial in several applications.
Some of the benefits are:
- Lower Latency: Faster processing of data translates to rapid responses.
Lower Bandwidth: Less transfer of data to the cloud, hence bandwidth saving and associated costs.
Higher Reliability: Processing locally can continue, even in the presence of an unstable internet connection.
Some common uses are as follows: - Smart Cities: Manage traffic based on local data from sensors.
- Healthcare: Real-time data analytics for better care of patients.
- Manufacturing: Track the status of machines in real-time to maintain efficient production.
All such benefits of edge computing make it one of the most important technologies for modern applications that depend on high-speed data processing.
Basics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing provides a great deal of services that can be remotely accessed through the internet. They include services for storage, networking, and software. Sound knowledge about the core concepts and benefits of cloud computing helps users and organizations in effective decision-making.
Definition and Core Concepts
Cloud computing is a technology which, in simple words, allows users to store, process, and access data and applications over the internet instead of locally on their personal servers or computers. There are three main models:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Users can rent IT infrastructure, like servers and storage.
Platform as a Service (PaaS): It provides a platform to the developer for developing applications without bothering about managing the hardware underneath.
Software as a Service (SaaS): The user basically accesses software applications over the internet, which are run remotely without the need for installation. These models make scaling and management of IT resources very easy.
Key Benefits and Uses
The main advantages of cloud computing are as follows:
It reduces the usage of physical hardware, thereby reducing the cost of maintaining hardware. Scalability: Scaling up and down of resources can be easily done according to requirements. Accessibility: From any device, provided there is an internet connection, data and applications can be accessed. Data storage, web hosting, and application development are some of the common uses. Many organizations in many different fields depend on cloud services to enhance efficiency and collaboration among workers.
Also Read :
- The Rise of Quantum Computing: What It Means for Technology
- The Future of Mobile Technology: Trends to Watch in 2024
- Blockchain Technology: Understanding Its Impact Beyond Cryptocurrencies
- Technology in Marketing 2024
- FAE Technology Quote