How to Design a Smart Building: Engineering Is the Process to Be Followed
Designing a smart building means planning all its aspects carefully and using high-end engineering technologies. The way forward in effective design of a smart building is the integration of systems for efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. A smart building is one that is fitted with different sensors and automation that help in efficiency, security, and user experience.
In this process, engineers get to choose the right material, systems, and technologies while ensuring that all components of a building are integrated to work together seamlessly. In this way, buildings become both functional and able to respond to changing users and environments.
Smart buildings are the future of the architecture and construction field. They stand out by their efficiency in satisfying users. Because technology is continually changing, the potential for innovation in building design has just grown farther and farther.
Key Takeaways
Smart buildings rely on integrated systems as the foundation that enables them to be efficient and sustainable. Technologies from the fundamentals of Engineering assure the adaptability and functionality of the space. Future designs will encompass evolving technology that is user-friendly and therefore offers ultimate user experience: Smart Building Design Basics
Smart building design connects advanced technology and engineering to develop spaces that enhance efficiency and comfort. Some of the key elements of the design include: understanding smart buildings, the role of engineering in the creation of smart buildings, and principles that define sustainable designs which enhance a building’s functionality.
Understanding Smart Buildings
Smart buildings optimize operations through technology and improve user experiences. Smart buildings consist of systems in place that control light, heating, cooling, and security. They use sensors, software, and data analytics to keep lots of conditions of situations monitored and optimized in real time.
For instance, smart thermostats can adjust temperatures autonomously by sensing occupancy patterns. Lights can be tuned to save energy when there is no person in a certain room. All these technologies coordinate with each other to finally produce a habitable and comfortable environment for residential and office spaces.
Role of Engineering in Smart Buildings
Engineering is the base of the development of smart buildings. Many engineering fields, such as electrical, mechanical, and civil engineering, are used side by side with the task to design and implement these systems.
It is only when the engineers make this possible that technology will perfectly synchronize with the building design. This goes a long way from the selection of suitable materials and systems, which can support several technologies, to the selection of the HVAC systems that have low energy demand, thereby providing good comfort and indoor air quality.
Engineers further evaluate the cybersecurity risks to safeguard smart systems from potential threats. It is proactive in this way, leading to safety and reliability in smart buildings.
Sustainable Design Principles
In smart buildings, sustainable design has the core objective of making a minimum environmental impact while improving efficiency. Some of the major ones include those of energy efficiency, water conservation, and renewable materials.
Energy-efficient designs may incorporate solar panels or green roofs to minimize reliance on nonrenewable sources of energy. Water conservation will be guaranteed through the fixing of water-saving devices and collecting rainwater.
Furthermore, most of these sustainable materials are deliberately taken from renewable or recycled resources, offering a far healthier environment without waste. A building whose core principles encompass this will be smart; but not just smart—it will be also environmentally responsible.
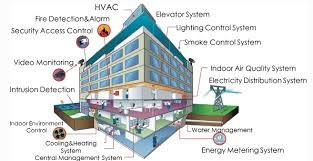
Modern Engineering Technologies
Advanced engineering technologies are at the heart of smart building functionalities. A couple of the principal areas include intelligent automation systems, energy efficiency technologies, and structural health monitoring. Each plays a critical role in creating efficient, safe, and user-friendly spaces.
Intelligent Automation Systems
The systems for intelligent automation are fundamental in the control and management of building operations. These are used to handle aspects such as lighting, heating, ventilating, and air conditioning, among others, in a manner that ensures comfort and optimality:
Key Features of Intelligent Automation Systems
Occupancy-sensing sensors that adjust settings based on occupancy. Central Control—remote management through mobile apps or dashboards. AI Integration—learns user preferences to enhance system responsiveness. This technology helps in saving energy and enhancing overall experience for the tenants. By ensuring that the systems work in tandem, smarter decisions can be made related to the use of resources.
Energy Efficiency Technologies
Energy saving technologies reduce the use of energy in a building. These technologies reduce the high cost of utility bills in buildings and energy utilization, which affects the environment.
Key Elements:
High Performance Insulation: A technology that aids the blockage of heat from exiting the building through the walls and windows during the winter season and retains the cool air inside in the summer season.
- LED Lighting: Used bulbs consume less energy compared to the regular ones.
- Smart Meters: Reads the amount of power utilised, thus making the owner of the building to drive strategies to reduce the various patterns of consumption.
Including such systems allows buildings to operate in accordance with energy standards and, at the same time, in a more sustainable manner. Efficiency is becoming an increasingly important focus both due to cost and concern for the environment.
Structural Health Monitoring
Structural Health Monitoring assures the integrity and safety of a building over the entire life of the structure. This uses sensors that detect the change in the status of the structure, which is critical especially when substructures are concerned.
Critical Elements:
- Vibration, stress, and deformation sensors
- Data analysis: Predicts possible problems by regular analysis of such data.
- Alert Systems: Offer real-time alerts in the event of detection of any structural abnormality. Inclusion of structural health monitoring helps to avert drastic repairs and ensure safety, offering peace of mind to both the owner and tenants of the building about their structures.
Also Read :
- The Rise of Quantum Computing: What It Means for Technology
- The Future of Mobile Technology: Trends to Watch in 2024
- Blockchain Technology: Understanding Its Impact Beyond Cryptocurrencies
- How to Repair External Hard Disk Not Detected
- Climbing technology