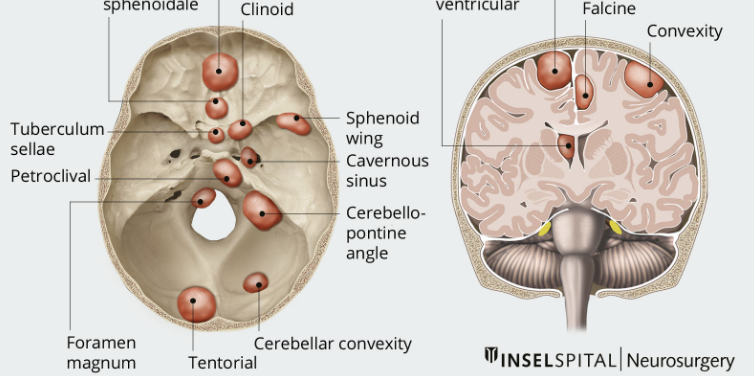
Neurosurgical MRI of the Brain: Techniques and Advances for Enhanced Surgical Accuracy The use of MRI in neurosurgery, especially in localizing brain tumors, has been an indispensable tool. With improvements in MRI, it can now generate detailed and very accurate pictures of the brain, hence allowing surgeons to pinpoint the tumor in question and effectively plan a course of treatment. It is because of this technology that surgical procedures have become safer and more successful.
Besides precision, MRI is also a non-invasive modality without the use of radiation; it is, therefore, preferred by both the patients and the doctors. An understanding of how MRI works and what role it plays in localizing brain tumors opens the door to a deeper appreciation of modern neurosurgical practices. It could be useful to any interested in either medical technology or brain health.
By realizing the impact that MRI has had on neurosurgery, one can understand how brain tumors are treated differently now. Such a combination of detailed imaging with refined techniques has significantly enhanced surgical procedures.
Key Points
- MRI provides detailed images that allow for tumor localization in the brain.
It is a non-invasive imaging modality and does not use radiation. - State-of-the-art MRI techniques enhance surgical planning and patient outcome. Principles of MRI Technology
- MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of the brain and other body parts. MRI is indispensable in diagnosing a variety of disorders, including brain tumors. Knowledge of principles and safety considerations can further enhance the effectiveness of utilizing MRI within the clinical practice.
Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI operates on the principle of aligning hydrogen atoms within the body using a very strong magnetic field, followed by sending radio waves through the body. The aligned atoms, being affected by these radio waves, give out signals that are received and transmitted to a computer for analysis and generation of detailed pictures of brain morphology.
Some of the factors affecting the quality of the resulting MRI images are as follows:
Strength of the magnetic field: Higher the strength, measured in Tesla, T, the better the quality of the image.
Coil design: Better resolution is achieved since the coils are designed to focus on certain areas of the body.
Sequence Parameters: These show different types of tissue that may suggest the presence of abnormal tissue, such as tumors.
MRI Safety and Suitability
Safety is an essential factor concerning the use of MRI. There are those patients who, because of certain implants or devices, cannot undergo the MRI procedure. The following are some of the things that need to be screened for:
Pacemakers
Cochlear Implants
Metal Fragments in the Body
Patients have to inform radiologists about their health issues in advance.
Even though MRI is generally safe, there are precautions. It includes the following:
Noise: The machine is quite loud; ear protection is provided.Enclosed Spaces: Some people may feel uneasy inside the scanner. Open MRIs are also used for patient comfort.
Knowing safety precautions and how MRI works will better enable a patient to make informed decisions about their treatment.
MRI Brain Tumor Localization
MRI has become quite indispensable in the localization of brain tumors. It aids in the planning of surgery, guides surgeons intra-operatively, and is helpful in the evaluation of post-operative results.
Pre-Surgical Planning and MRI
Preoperatively, MRI scans determine the exact location and size of a brain tumor. High-resolution images will help the physician better detail the tumor’s relationship to nearby critical brain structures.
Doctors identify the type of tumor through a specific MRI sequence, including T1-weighted and T2-weighted images. This information is useful in selecting the most suitable surgical approach.
fMRI may identify areas of particular value in the brain, like areas involved in speech or movement. This may be important for surgeons to avoid damaging important functions.
Intraoperative Guidance of Surgery
Intraoperative MRI may update tumor localization during surgery. Real-time imaging offers better delineation of tumor structure during an operation.
The application of iMRI in this way ensures that no part of the tumor is left behind, reducing any residual cells that may remain behind. The immediacy of the response provided by the technology assists the surgeon in refining their technique.
iMRI allows surgeons to follow the condition of the patient throughout the surgical procedure, thus enabling them to act quickly in case of complications. This can be highly variable and may bring about better surgical results.
Postoperative Evaluation and Follow-Up
MRI has become crucial postsurgery to assess the outcome of tumor removal and to search for recurrences. Indeed, it is after the post-surgical scan that it shows whether any tumors persisted or new ones have evolved.
Regular follow-up MRI studies enable the healthcare provider to observe the patient’s improvement and, when possible, the early detection of problems. They can identify changes within the brain tissue that may indicate further complications or the need for additional intervention.
The use of MRI in performing these tests will afford the physicians valuable information on which to base decisions about ongoing management. This makes it an important diagnostic tool both in the immediate and long-term treatment plan.
Also Read :
- MRI Applications in Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery
- MRI-Guided Neurosurgery: Current Trends and Innovations
- The Role of Functional MRI in Neurosurgery
- The Impact of Diffusion Tensor Imaging on Neurosurgical Procedures
- Neurosurgical Tumor Resection and MRI Imaging
- Advanced MRI Techniques in Neurosurgical Planning