Neurosurgical Approaches in MRI for Glioma Management: Optimizing Treatment Strategies and Outcomes
Neurosurgery is very essential in the management of gliomas, tumors arising in the brain. The introduction of MRI technology enhances surgical planning and execution, leading to improved patient outcomes. It offers very clear details about the brain that help neurosurgeons find their way around this small, complex area with minimal injury to healthy tissue.
Advanced neurosurgical navigation systems integrate to improve precision in glioma resections. Such tools are used for tumor localization and the assessment of brain structures surrounding the tumor in real-time by surgeons. This approach not only heightens the possibility of successful tumor removal but also helps in conservation of essential functions of the brain.
Innovative surgical techniques continue to evolve and render the management of glioma even more efficacious. Coupled with state-of-the-art imaging, judiciously developed techniques allow for the individual treatment of a patient in a specific condition. This article reviews some of those advances and their place in neurosurgery.
Key Takeaways
MRI helps provide optimum surgical planning for the treatment of glioma.
Advanced navigation tools improve accuracy in tumor removal.
Evolving techniques improve the outcomes for patients with glioma management.
Principles of Neurosurgical Navigation
Neurosurgical navigation significantly affects the successful management of gliomas. Knowledge of brain anatomy, development of imaging, and functional MRI contribute to improved accuracy in surgery and better patient outcome.
Anatomy and Physiology of Brain Gliomas
Gliomas are tumors originating from brain glial cells, which are important in the support and protection of neurons. These can be different in their type and grade, which further influences their behavior and treatment modality.
The important types of gliomas include
Astrocytomas arise from the astrocytes themselves and may be low grade or high grade. Oligodendrogliomas are derived from oligodendrocytes; generally, these have a good prognosis. Ependymomas arise from ependymal cells; these may occur in ventricles.
The location of gliomas is important in guiding the surgery. The regions that are adjacent to vital structures such as the motor cortex or speech areas need to be well strategized. Knowledge of the tumor’s position and its relation with the brain helps in conducting safer and more adequate surgeries.
Advancement in MRI Technology
The recent advance in the technology of MRI has brought changes in neurosurgical navigation. High-resolution MRI and diffusion tensor imaging techniques provide clearer images of brain structures.
Following are some of the key features of new MRI technologies:
- Functional MRI (fMRI): It maps the activity of the brain by detecting changes in blood flow. This feature helps surgeons locate critical functions before surgery.
- 3D Imaging: It outlines models of detailed structures of the brain, which enables tumor localization and surgical planning.
These advances provide an increased ability to visualize complex brain anatomy. These help in differentiating between tumors and healthy tissue-a factor that is utmost during surgery.
Integration of Functional MRI
Functional MRI has now played a significant role in neurosurgical navigation to outline the brain’s functioning map. It serves during the identification of areas of movement, speech, and other crucial activities.
The surgeons can then use such data provided by fMRI to:
- Avoid areas that are not to be touched during the operation.
- Do better preoperative planning.
- Customize the approaches according to individual brain mapping.
The inclusion of functional imaging in navigation systems has been increasingly ensuring that surgical operations are safer. Moreover, it enhances personalized strategies for the removal of gliomas while preserving vital brain functions.
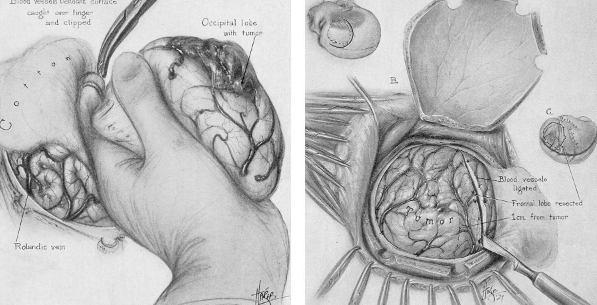
Surgical Techniques in Glioma Resection
Surgical techniques play a crucial role in glioma resection to achieve maximum tumor removal while preserving brain functions. Key features include pre-surgical planning, intra-operative imaging using state-of-the-art modalities, and outcome analysis following surgery.
Preoperative Planning
Glioma surgeries require ample preoperative planning. As a rule, surgeons carry out critical assessments in the form of MRI scans that locate and identify tumor location and size. These images allow one to conceptualize the relationship of the tumor to surrounding brain structures.
Multidisciplinary teams often meet and discuss the surgical approach. A neurosurgeon, radiologist, and neurologist – teams that combine to create the best strategies.
It can also be utilized by surgeons to map regions of the brain responsible for vital functions such as speech and movement. This is done so as to minimize damage to healthy brain tissue during surgical procedures.
Intraoperative MRI Guidance
Intraoperative MRI guidance is an important tool available to the surgeon during glioma resection. The surgeon is thus able to visualize the brain in real time with the use of a live MRI scan. This technology allows for more precise tumor removal.
Whereas the surgery is in process, the intraoperative MRI helps the physician verify whether the tumor has been totally resected. In case the residual tumour tissue is found, surgeons can remove it immediately.
This minimizes the chances of recurrence of cancer. It also improves safety of the surgical procedure and brings about better patient outcomes.
Postoperative Assessment
Assessment postoperatively is among the key concerns in the treatment of glioma. Imaging studies, including MRI or CT scan, are conducted on the patients after surgery. These studies help the physician evaluate the effectiveness of surgery in removing the tumor and also establish whether any residual tumor tissue is present.
These images are further reviewed cautiously by the surgeons along with the care team. They check for complications such as swelling or bleeding.
The recovery of the patient is closely monitored. Neurologists will examine cognitive and motor functions for changes. These shall enable one to plan further treatment if need be.
Also Read :
- MRI in the Management of Cerebral Aneurysms and Neurosurgical Clipping
- Imaging Biomarkers in MRI for Neurosurgical Outcomes
- MRI in Hydrocephalus and Neurosurgical Shunt Placement
- Advanced MRI Sequences in Neurosurgical Interventions
- Functional Connectivity Mapping in Preoperative Neurosurgical Planning