Neurosurgical Tumor Resection and MRI Imaging: Development and Optimization of Diagnostics in Therapy.
Surgical resection of the tumor by neurosurgery is an important method for the treatment of brain tumors. This kind of complex surgery removes as much of the tumor as possible while saving as much healthy brain tissue as possible. MRI imaging is important in planning and guiding these surgeries. MRI visualizes the tumor and its relation with surrounding structures, making these operations safer and more effective.
The marriage between tumor resection and MRI imaging is very crucial in improving the patient’s outcome. MRI scans provide enough detail such that surgeons make appropriate decisions during the operation. This partnership improves accuracy, thereby reducing risks and complications associated with the surgery.
So, more development of neurosurgery will still increase the importance of MRI. This imaging technique gives such clarity and precision that the approach to surgery can be changed, less invasive, and more effective.
Key Words
- The goal of neurosurgical tumor resection is to safely remove a tumor while preserving healthy tissue.
- MRI imaging is paramount in guiding surgical decisions to optimize outcomes.
- Improvement in neurosurgical procedures with advances in imaging technology.
Principles of Neurosurgical Tumor Resection
Neurosurgical tumor resection is a rather complex process that is based on the main idea of several perceptions. It is the surgical procedure meant for the removal of tumors either from the brain or from the spinal cord by taking the aid of accurate imagery and plans.
Principles of Neurosurgery
The key concept of neurosurgery is the resection of tumors with minimal compromise of healthy normal tissue around the tumor site. Neurosurgeons need to take into consideration tumor size, tumor type, and tumor location.
They utilize highly developed techniques, which include fluorescence imaging to help delineate the tumor cells during surgeries.
Patient Safety
The patient’s vital signs and brain activity are monitored by surgeons during the operation. The surgeons use their knowledge of anatomy to try working between the structures of the brain, inflicting as minimal damage as possible in an attempt to remove the tumor.
Types of Neurosurgical Tumors
Tumors accessible by neurosurgery may be broadly placed into one of two categories: primary or metastatic.
The primary tumors arise directly in the brain or spinal cord and involve gliomas and meningiomas.
Metastatic tumors of the brain originate from tumors elsewhere in the body, such as from lung or breast cancer.
Each carries a different prognosis and may call for different treatments. Treatment options also depend on the tumor’s grade-diagnosed as either low or high. Low-grade tumors can be slower growing and may be treated less aggressively than high-grade tumors, which are often responsive to more aggressive therapies.
Surgical Planning and Approaches
The planning for surgery is crucial for successful tumor resection.
Before surgery, imaging tests, such as MRI, provide detailed views of the tumor’s location and shape.
Surgeons plan an effective approach to the tumor.
Common approaches include:
Craniotomy: Opening up the skull to reach the brain.
Endoscopic surgery: Performing a surgery using small instruments through tiny openings.
The surgeons assess the risks and discuss them with the patient. For recovery, post-operative care is necessary. It involves monitoring complications such as infection or neurological deficits.
Better planning and proper execution is definitely associated with better results in neurosurgical tumor resections.
Role of MRI Imaging
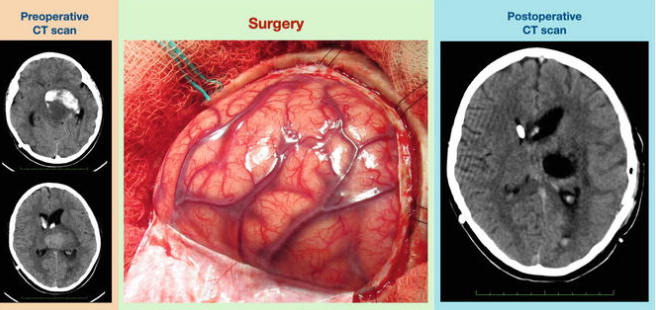
MRI thus plays a very important role in the management of neurosurgical tumors. It aids in the diagnosis, guides through the surgery, and is done post-operatively to assess the results. Accurate imaging will, therefore, lead to sound clinical judgment by the doctors during the course of treatment.
Preoperative MRI
It is crucial in the preoperative planning of neurosurgery. It provides a clear outline of the size and location of the tumor, as well as its nature. With this information, surgeons are able to get an idea about the direction of surgery.
MRI would also depict the brain structure surrounding the lesion, helping surgeons to have an idea about the risk involved. MRI can identify benign and malignant tumors, which may affect treatment options.
An improved quality of MRI is realized with the support of contrast agents. Such improvement helps in identifying tumor tissue from healthy brain tissue. In short, preoperative MRI has a tremendous and significant role in effective surgical planning.
Intraoperative MRI Technology
The intraoperative MRI system allows real-time imaging at the time of surgery. This innovative technology helps surgeons in locating the tumor when performing the surgery. It makes sure they resect as much of the tumor as possible with minimal damage to the healthy tissue.
Intraoperative MRI can change the surgical approach during live images. Surgeons will be able to make readjustments if the tumor is larger or more complicated than initially thought. The flexibility allows for better outcomes.
Intraoperative imaging helps to reduce the possibility of residual fragments being left from the tumor. It may reduce the chances of recurrence by improving patient outcome.
MRI Postoperative Evaluation
MRI after surgery is important during the evaluation of whether or not removal of the tumor has been effective. This would give the medical practitioner the opportunity to go through whether all the cells of the tumor had been removed. This may entail scanning of the patient a few days after surgery.
Scans after a surgical operation can also be used in checking for complications such as bleeding or swelling. It is very fundamental in monitoring recuperation of the patient’s process.
When follow-up MRIs are done regularly, the early signs of recurrence of the tumors will be outlined. That way, interventions will be timely, leading to better overall management of the patients.
Also Read :