MRI of Spinal Tumors: Techniques and Insights in Neurosurgical Evaluation Spinal tumors diagnosed through MRI studies remain a very important modality. Such studies give extremely useful, detailed images to provide a better understanding of the size, shape, and precise location of tumors-an essential factor in treatment planning. Since spinal tumors may affect spinal cord function, accurate diagnosis and assessment are really critical for achieving favorable neurosurgical outcomes.
However, MRI technology in application is poised to grant neurosurgeons greater insight into the same case. That it is a non-invasive imaging technique with the added advantage of delineating soft tissues better than any modality is reassuring. Such clarity will lead to the proper judgment on the most feasible approach to surgery or other options available.
Improved MR techniques continue to enhance the capability of diagnosing spinal tumors. With advances in imaging quality and processing, neurosurgical assessment is surely bright. More accurate and timely information can enable better management and planning for the patients.
Key Takeaways
- MRI plays an important role in the assessment and treatment management of spinal tumors.
- Advanced MRI techniques improve the accuracy of diagnostics.
Good assessment leads to good neurosurgical outcome. MRI Technology in Spinal Tumor Analysis
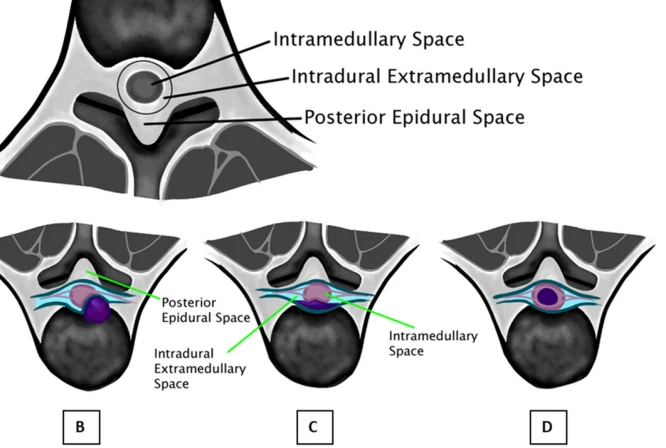
MRI has become very important in the investigation of spinal tumors by providing an accurate location, surgical planning, and determination of the extent of tumor infiltration.
Advancement of MRI Techniques
In recent years, there have been advancements in the way physicians view spinal tumors using MRI techniques. High-field MRI systems provide sharper images with better contrast resolution compared to older systems. This leads to better detectability of small or early-stage tumors.
Other key techniques include functional MRI and DWI. The former technique measures changes in blood flow to perform brain mapping regarding function, while the latter monitors the movement of water molecules within tissues. All these techniques help in understanding tumor characteristics and behaviour.
Role of MRI in Preoperative Planning
It is an essential investigation done for preoperative planning in spinal tumor surgeries. It gives a more precise size and shape of the tumor, thereby helping surgeons decide on the best surgical approach.
MRI can outline tumor relations to surrounding tissues, thus preventing intraoperative injury to vital structures like nerves and vessels. This also provides information on the necessity of adjuvant therapy in the form of radiation therapy.
Assessment of the Extent of Tumor and Involvement
The extent of a spinal tumor is of paramount importance for treatment. MRI accurately depicts the extent to which a tumor has invaded the spinal column and its surrounding structures. It is highly essential in staging the tumor and planning a treatment regimen.
Radiologists examine the MRI images for the size of the tumor and other features, including involvement of the spinal nerves. It also looks for any compression or infiltration into surrounding tissues. These analyses help in estimating the likelihood of success of surgery and possible outcomes in the patient.
Implications for Neurosurgical Outcomes
MRI of spinal tumors plays an important role in the outcome determinants of neurosurgery. The detail of the images will reflect in most of the aspects of surgery, whether it be accuracy, follow-up of patients, or long-term outcome.
Correlation with Surgical Precision
MRI significantly enhances surgical precision. Such detailed pictures locate the exact position of the tumor and help the surgeons understand its relationship with the surrounding tissues. This is very important for minimal damage to healthy structures during surgery. Better imaging enhances better preoperative planning that may lead to successful tumor resections.
These surgeons often use various advanced MRI techniques such as functional MRI and diffusion tensor imaging to map critical neural pathways. In so doing, they are able to avoid critical areas and minimize complications. The improved precision of surgery correlates directly with better patient outcomes, including less postoperative pain and shorter recovery times.
Postoperative Monitoring
MRI proceeds after surgery to play an important role in the follow-up of the patient’s condition. Regular follow-up scans help identify residual tumor tissue or recurrence. This becomes essential in early detection, necessary for the initiation of further treatments, including radiation or additional surgery.
It is also used in the assessment of complications such as infection and fluid accumulation. MRI postoperative care will help healthcare teams manage any complication that may arise from surgery on time. This is the continuous evaluation which is important in the management of patients for their recovery to be optimized effectively.
Long-term Prognosis for Patients
The involvement of MRI goes as far as the long-term outcome of patients undergoing surgery for spinal tumors. Some studies have tried to demonstrate improved survival rates and living standards owing to accurate imaging. Patients with accurate preoperative and postoperative MRI findings tend to have fewer complications.
Studies indicate that such detailed imaging allows for appropriate treatment planning and, hence, better health outcomes. A well-planned treatment will minimize discomfort and will keep the patient informed, thus allowing for greater compliance in follow-up treatments. MRI can help in maintaining the long-term follow-up in order to maintain the awareness of the patients about their ailments and enable timely intervention if required.
Also Read :
- MR Angiography in Neurosurgical Management of Vascular Malformations
- The Role of MRI in Neurosurgical Trauma Care
- MRI Imaging in Neurosurgical Treatment of Brain Metastases
- MRI and Image-Guided Neurosurgical Biopsies
- Functional MRI in Neurosurgical Research