The insight and application of this important diagnostic tool may better realize the role of MRI in cranial nerve disorders and neurosurgical treatment. This imaging modality has been highly useful in viewing nerve structures in great detail. Such a view facilitates identification of problems in nerves, such as tumors, lesions, or other abnormalities. The realization of how MRI helps attain these medical conditions may make all the difference in the results of patient outcomes and treatment options.
As neurosurgeons continue to apply MRI in diagnosis, their ability to target interventions more precisely for particular disorders of the cranial nerves will also be improved. This sort of personalization has the potential to optimize both safety and efficacy. This requires keeping abreast of the latest technical developments in MRI technology and techniques by those active in the treatment of these disorders.
It is not only about diagnosis; MRI also goes hand in hand in planning surgical strategies. Diagnosis coupled with planning enables healthcare providers to navigate those sensitive structures of the nervous system even better.
Key Takeaways
- MRI provides detailed images that are useful in diagnosis, hence facilitating the identification of disorders in cranial nerves.
- Treatment plans are tailor-made, enhancing safety and effectiveness during surgery.
- Emerging technologies in MRI continue to advance the care given to the patients.
MRI Technology in Diagnosing Cranial Nerve Disorders
MRI plays an important role in the diagnosis of cranial nerve disorders. It gives detailed structure both of the brain and its surrounding tissues and, therefore, aids in the diagnosis of the abnormalities of the nerves. The subsequent sections discuss basics related to MRI, cranial nerve anatomy as viewed on MRI, and advanced techniques in the field.
Imaging Basics of MRI
MRI or Magnetic Resonance Imaging is a method of obtaining detailed pictures of organs and tissues in the body using strong magnetic fields combined with radio waves. It does not rely on harmful radiation; thus, it is a safe modality for imaging.
MRI basically aligns hydrogen atoms in the body and then uses a magnetic field to create images. These kinds of images can show abnormalities that may affect cranial nerves, such as tumors or inflammation.
This clarity of the pictures taken enables the doctors to clearly present and diagnose the disease. MRI will be able to view soft tissues, which is quite significant in diagnosing cranial nerves.
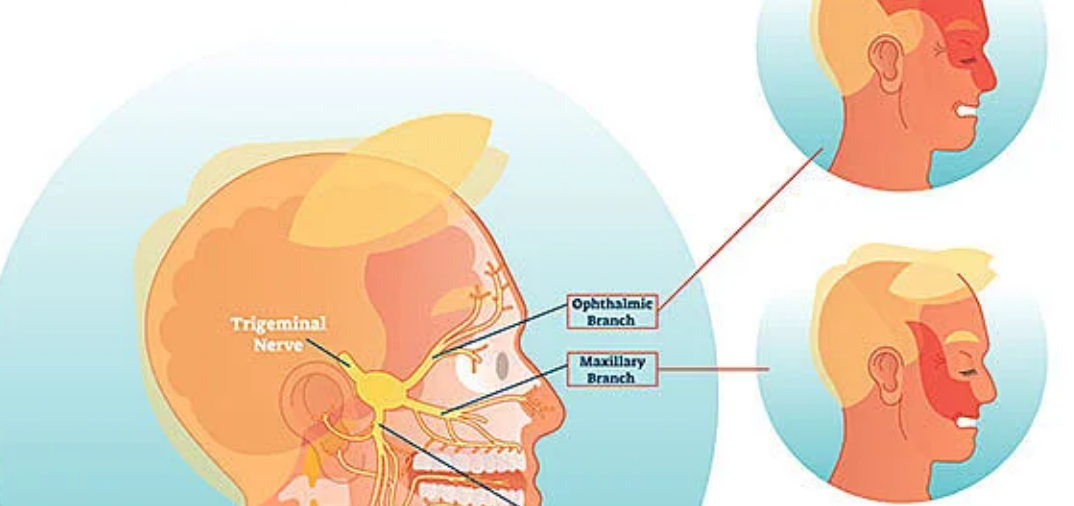
Anatomy and MRI of Cranial Nerves
Cranial nerves are necessary in most of the activities within our body, such as movement and sensation. There are 12 pairs of these nerves inside of every living thing each performing a different function. MRI will allow viewing these nerves with their pathways.
With MRI for viewing cranial nerves, radiologists are able to identify any changes either in their shape or position, both of which can be indicative of an abnormality. Many compression or lesions are thus visible in images.
Knowledge of cranial nerves’ anatomy helps in identifying the normal and abnormal during a scan. It is also improving the diagnostic process.
Advanced MRI Techniques
Advanced MRI techniques give a potential in the study of cranial nerves. One such technique is DTI, which maps water movement in brain tissue. This depicts the integrity of the nerve tracts.
The method of fMRI involves a measurement of the brain activities by way of changes in blood flow. This technique helps understand the functioning of cranial nerves while performing some task.
These advanced methodologies enhance diagnostic accuracy. They enable the clinician to visualize structural as well as functional impairments of cranial nerves, thus guiding toward appropriate treatment.
Also Read :