The Role of MRI in Neurosurgical Treatment of Pituitary Tumors: Improvement of Diagnosis and Surgical Outcome
MRI has been very important in the treatment course regarding pituitary tumors. It helps doctors visualize the size and location of a tumor. Therefore, it aids in appropriate diagnosis and treatment. By providing detailed images of the brain and surrounding structures, MRI allows neurosurgeons to effectively target a tumor while limiting damage to healthy tissue.
MRI not only enhanced surgery outcomes but also improved the safety of the patients from the complications arising. This modern imaging technique provides the possibility of regular follow-up on changes in tumors for treatment adjustments. Further, MRI therefore allows doctors to treat their patients in a more individualized manner.
Understanding the role of MRI in neurosurgical treatment of pituitary tumors is important to the patients and their families on the journey. The information obtained from MRI may serve to make an informed decision, enhancing quality care.
Take Home Messages
- MRI provides accurate images that are important for diagnosis of a pituitary tumor.
- It enhances surgical planning and patient safety during treatment.
- Regular MRI follow-up may lead to better management of tumor changes.
Principles of MRI in the Evaluation of Pituitary Tumors
MRI has continued to play a vital role in the study of pituitary tumors. This is because it produces highly detailed images of not only the brain but also structures surrounding it, thus helping doctors make informed treatment decisions.
Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI uses a strong magnet combined with radio waves to generate images. A magnetic field is produced by this scanner in which hydrogen atoms in the body align. These hydrogen atoms emit signals when these radio waves are turned off, which the MRI scanner detects.
It processes these signals to produce a series of images. Some MRI sequences highlight specific tissue types and pathologies. In all pituitary tumors, high-resolution images are quite useful in the demarcation of tumor size and location, as well as in assessing its impact on surrounding structures.
Advantages of MRI for Pituitary Lesions
There are several advantages offered by MRI in pituitary neoplasms. High contrast images of soft tissues provide better delineation between normal and neoplastic tissues.
Because MRI does not use ionizing radiation, as CT scans do, it is a much safer modality for the patient. High detail in these images allows for the detection of very small tumors, and detail extension into adjacent structures.
Besides structural information, MRI can also offer functional information using advanced techniques. For example, dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI provides information on tumor blood flow and implications on tumor behavior.
MRI Techniques and Protocols
Most MRI techniques for the pituitary gland are of value, but the most usual protocols involve T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences.
T1-weighted images are useful in detailing the pituitary gland’s anatomy. T2-weighted images are obtained to outline edema or inflammation at areas surrounding the tumor.
This can be enhanced by the administration of gadolinium contrast, which better delineates the tumor and its margins. Additional optimization of sella turcica assessment-the location of the pituitary gland-can be provided by specific slice orientations.
These techniques ensure that the assessment of pituitary lesions is thorough, thus helping the planning of surgery and follow-up studies.
Clinical Applications and Outcomes
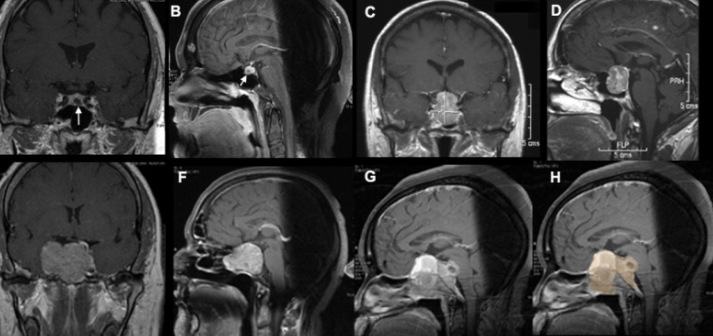
MRI has, meanwhile, been integral in the management of pituitary tumors by allowing preoperative planning and intraoperative strategy and by providing indispensable information useful during follow-up after surgery. Each stage benefits from the detailed imaging of MRI because it provides valuable information about the nature of the tumor.
Preoperative Characterization of Tumor
MRI, preoperatively, outlines the size, shape, and exact position of the tumor. This imaging can include whether structures like the optic nerve surrounding them have pressure imposed on them by the tumor.
Key features include:
- Tumor Type: Establishing whether the tumors are adenomas or other types.
- Presence of Invasion: Whether or not tumor tissue has grown into the surrounding structures.
- Hormonal Activity: Some tumors can even produce hormones that can influence other bodily functions.
This detailed information further guides surgical approaches and techniques, enabling personalized treatment plans.
Intraoperative MRI
Presently, iMRI during surgery is an increasing trend. It allows surgeons to see the tumor in real-time during the surgical activity.
The advantages of using iMRI include:
- Immediate Feedback: Surgeons are able to confirm completeness of tumor removal.
- Changing in Strategy: In case residual tumor detection, surgical plans can be changed on the spot.
- Reducing Complications: Better visualization in avoiding damage to critical brain structures.
The use of iMRI may improve surgical outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Postoperative Surveillance and Recurrence
Even post-surgery, MRI has an important role in monitoring recovery. Routine scanning helps identify early signs of tumor recurrence.
Important features of postoperative care include follow-up schedule, usually frequent MRI examinations every 3 to 6 months; follow changes, whereby the postoperative image with previous scans is compared to see if anything new has grown; hormonal testing-as continued assessment of hormone levels may also give an indication of the possible return of the tumor. This watchfulness ensures that in case there is a recurrence, it will be early enough to bring about good results with treatment.
Also Read :