Deconstructing the Basics: How Renewable Energy Works
Renewable energy resources, being peculiarly important in the modern world, are under increased scrutiny due to questions revolving around climate change. It works through the collection of natural processes – sunlight, wind, and water – and then converting them into power, leaving resources intact. This form of energy not only cleans up harmful Earth emissions but acts as a strong backup for future generations.
Understanding how each of these renewable systems functions forms the very basis of appreciating their importance. Every technology, from the solar panels converting sunlight into electric current, to the wind turbines, which do basically the same with the energy of the wind, is vital in a cleaner energy world. Continuous improvements within these technologies have made renewable energy approaches more available and efficient than at any point in history.
Knowledge and awareness of renewable energy are taking a front seat as people work for a greener world. A proper understanding of the concept will greatly show that changing to these sources of energy will bring a brighter future and complete freedom in terms of energy.
Key Takeaways
- Renewable energy is generated from natural resources.
- New technologies improve energy efficiency and access.
- Understanding renewable energy properly is important to reach a sustainable future.
Introduction to Renewable Energy
One of the main fields of interest of people who aim to, or wish to, reduce dependence on fossil fuels is renewable energy. It encompasses different types of energies by making use of natural processes in generating power.
Defining Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is generally derived from resources that are usually replenished by nature. This means they regenerate at a very fast rate and will never run out over human time frames. Common ones include sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat.
These energy sources can tremendously reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Thus, they are an aid in the fight against climate change and in the assurance of environmental sustainability. Renewable energy is very key on the pathway to a clean energy future.
Types of Renewable Energy
There are a number of significant types of renewable resources in common use:
- Solar Energy: Collected from sunlight by photovoltaic cells or solar panels.
- Wind Energy: This is produced through wind turbines, which convert the movement of air into electricity.
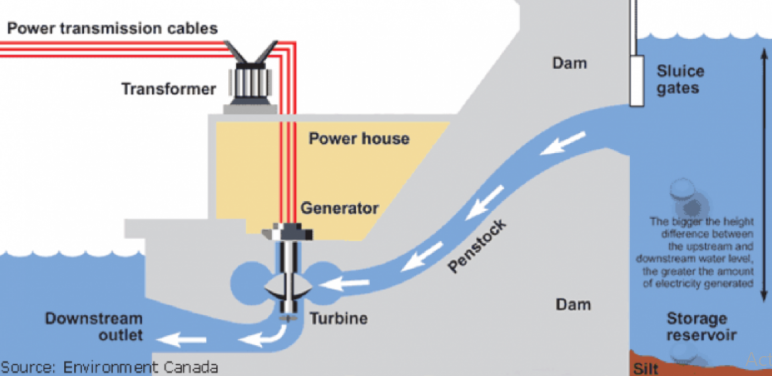
- Hydropower: Resulted from the use of energy created by moving water, often as a result of creating dams.
- Biomass: Created from organic matter such as wood and agricultural crops or waste.
- Geothermal Energy: Derived from the Earth’s interior heat, typically extracted through wells.
Each of these sources has different advantages and disadvantages. The combination of these sources enables various commitments to the demands on energy supplies using renewable resources.
Renewable Sources Produce Power
The generation of power from renewable energy sources is normally accomplished by a particular technology:
- Solar Panels: Convert sunlight into electricity with photovoltaic cells.
- Wind Turbines: Blades of the turbines rotate by wind action to actuate generators to generate electricity.
- Hydroelectric Plants: Collected water from the reservoirs; therefore, water flow through the turbines develops the generation of power. Biomass Power Plants: Organic material is usually burnt or otherwise transformed into steam to drive the turbines. Geothermal Plants: Steam generated from heated underground water acts on driving turbines.
These technologies convert natural energy into usable electricity. Each of them assures different efficiencies and costs, with different environmental impacts, and hence their rates of adoption are different across the world.
Technological Innovations and System Integration
Renewable energy is one of the fastest-evolving industries. Newer technologies and improved integrations with existing systems are making it increasingly viable. This section describes the recent developments in renewable technologies, their interface with the power grid, and the impact of policies and economics.
Improvement in Renewable Technologies
The recent improvements of renewable energy technologies are remarkable. Solar panels, for example, are much more efficient since there are some models which convert over 22% of sunlight into electricity. And designs for wind turbines are getting better-which with less wind can result in even higher output.
These innovations in energy generation, such as floating solar farms, make use of unused water surfaces. This contributes to minimizing land usage while harnessing energy. Other technologies, like the lithium-ion battery, are being developed to provide better energy storage and management. Cumulatively, these innovations make renewable sources practical and effective.
Grid Integration and Storage Solutions
Electrical power must increasingly use renewable sources. Smart grids are smart because of their improved monitoring and control of energy flow through the use of technology, allowing better balancing of supply and demand.
Energy storage systems, such as advanced batteries and pumped hydro storage, enable excess energy to be set aside for use at a later time. This infrastructure flexibility supports the intermittency of energy sources, such as solar and wind. This further enables microgrids to operate in island mode, enhancing energy reliability and efficiency even more at the local levels.
Policy and Economic Roles
Renewables are a source greatly influenced by growth in renewable energy policies. Tax credits and grants to incentivize green technologies increase investments in these emerging industries. Such incentives will greatly reduce costs to consumers and businesses in transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Economics also has its role. The continuously falling costs of technologies make the competition between renewable energy and fossil fuels possible. As the price of energies begins to take a turn, people start considering options for sustainability. Understanding this policy-economic-technology link is essential to the future of renewable energy.
Also Read :
- Harnessing the Power of Nature: The Future of Renewable Energy
- How Renewable Energy Technology is Gaining Ground in South Africa
- Renewable Energy Engineering: Designing Sustainable Power Systems
- Sustainable Engineering: Innovations in Renewable Energy
- The Environmental Impact of NFTs and Crypto Mining: Facts vs. Myths