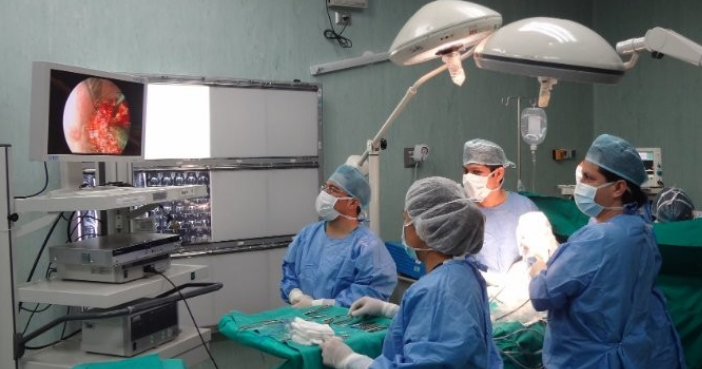
Minimally invasive neurosurgery is the future behind the curtain of how brain surgeries are now being performed. Advanced technology allows surgeons to operate with greater precision and touch as little as possible in the patient’s body. Besides reducing recovery time, this approach also lowers the risk of complication.
The frontiers of these changes have so far been the innovations in state-of-the-art imaging and special tools. These allow for more effective procedures than hitherto thought to be too risky or complicated. As the techniques continue to evolve, so too are the ways through which the treatments for neurological conditions are performed in a safer and faster fashion.
Therefore, this area of study has a bright future and can change some aspects of patient treatment. Doctors are striving to ground their practice on less invasive procedures for the better outcome and quality of life of a patient.
Key Points
- Minimally invasive procedures involve shorter periods of recovery.
- New equipment allows surgeons to conduct operations with higher accuracy.
- New frontiers in neurosurgery will increase patients’ safety.
Neuronavigation Advances
Recent neuronavigation techniques have developed to such an extent that surgeries are now safer and more precise. The technologies of finding the most delicate spots in the brain are key, thus making it easier for surgeons to cure patients with more effect. The section will explore two major developments: integration with augmented reality and high-definition fiber tractography.
Integration with Augmented Reality
Augmented reality now revolutionizes intra-operatively what surgeons perceive as their view of the brain by overlaying real-world views with digital images and helps in the highlighting of structures that are important.
AR could be used by surgeons to plan procedures well in advance. They can simulate surgery and rehearse the most difficult parts of it. Real-time updates using this technology might be possible; even changes that may come up unexpectedly during the operation can be easily managed.
AR enhances the accuracy of neuronavigation systems, therefore minimizing the possibilities of complications. It enhances the vision of surgeons in order to move with ease through sensitive brain tissues.
High-Definition Fiber Tractography
High-definition fiber tractography or HDFT yields high-resolution pictures of neural tracts. This modality helps the surgeon understand how various areas of the brain connect.
HDFT uses advanced, sensitive imaging techniques such as DTI to give a higher resolution mapping of the brain fibers. With this facility, surgeons can delineate the specific area of the brain that should be preserved during the course of surgery.
This becomes highly important in maneuvers around sensitive structures of the brain responsible for movement or speech. HDFT refines neuronavigation and allows safer, more selective approaches in minimally invasive neurosurgery.
Also Read :