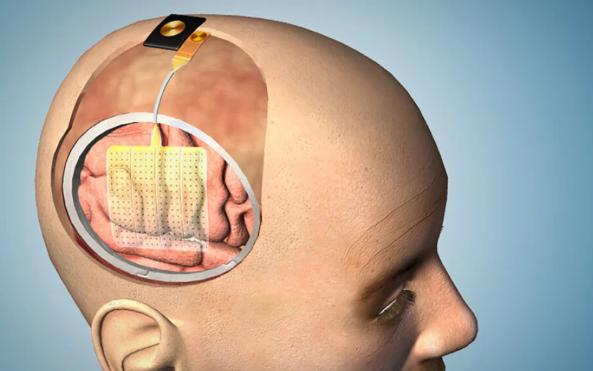
Spotlight on Brain Mapping: A Vital Tool in Neurosurgery
In the ever-evolving field of neurosurgery, precision and accuracy are key to successful outcomes. The brain, being a complex and delicate organ, requires utmost care during surgical procedures to preserve its myriad functions. One of the most revolutionary advancements in neurosurgery is brain mapping-a technique that has revolutionized the way surgeons approach brain surgeries. The importance of brain mapping, different techniques involved, and how this enhances safety and effectiveness in neurosurgical procedures are reviewed here.
1. What is Brain Mapping?
Brain mapping is a comprehensive process used to create detailed maps of the brain’s structure and functions. It helps neurosurgeons identify and preserve critical areas of the brain responsible for essential functions such as speech, movement, and memory during surgery. By accurately locating these regions, surgeons can avoid damaging them, thereby minimizing the risk of post-operative complications and improving patient outcomes.
1.1. Purpose of Brain Mapping
The general aim of brain mapping is to enhance accuracy during surgery and safely remove a brain tumor, lesion, or other abnormality without damaging any important brain functions. This technique is considered important, especially when the site of surgery is near or involves eloquent areas of the brain, that is, those parts of the brain responsible for vital functions.
2. Techniques Used in Brain Mapping
Different techniques, advanced ones, are applied to the mapping of the brain; all have their own specific benefits concerning the brain’s anatomy and functions. Non-invasive imaging technologies provide an insight that helps intraoperative procedures provide real-time information for the surgeons in their surgeries.
2.1. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Functional MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow. When certain parts of the brain are active, they require more oxygen, and as a result, more blood flows to those areas. fMRI captures these changes, thus enabling surgeons to visualize active brain regions associated with specific tasks.
Application: fMRI sees broad applications in pre-surgical planning, especially in the mapping of areas of the brain responsible for language, motor functions, and sensory processing. This helps surgeons plan safer surgical routes.
2.2 Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
DTI is a kind of MRI used to map white matter tracts’ courses in the brain. These tracts are pathways communicating between different brain regions. With DTI, neurosurgeons get more information about these tracts and ways to avoid damaging them during a surgery.
Application: DTI normally finds its application in cases involving brain tumors and epilepsy surgery for maintaining white matter tracts integrity for optimum outcomes post-surgery.
2.3. Intraoperative Cortical Stimulation
Intraoperative cortical stimulation is a technique that is used in awake brain surgery to directly stimulate the desired area of the cortex. Surgeons, based on the responses, will locate and avoid damaging those vital areas responsible for motor and language functions.
Application: This technique is especially helpful during surgeries of brain tumors or epilepsy, wherein immediate feedback helps in not damaging important functions.
2.4. Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
MEG measures the magnetic fields generated by neural activity in the brain and provides high temporal resolution of brain activity. It is also used in localizing functional areas of the brain involved in sensory and motor functions.
Application: MEG is combined with other imaging methods to provide an overall map of brain activity and for the planning and execution of neurosurgical procedures.
3. Role of Brain Mapping in Neurosurgical Procedures
Brain mapping significantly contributes to various neurosurgical procedures, including maximizing safety and efficacy. Following are some important aspects wherein brain mapping is absolutely essential:
3.1. Surgery for Brain Tumors
Brain tumors often develop in or very close to highly important areas of the brain. Brain mapping enables neurosurgeons to discern tumor tissue from essential normal brain tissue so that they can perform as complete a removal of the tumor as possible while preserving important functions.
Example: Preoperative fMRI can locate motor and language areas around a tumor and thus help plan a safer surgical approach.
3.2. Epilepsy Surgery
Brain mapping in medication-resistant epilepsy patients helps to locate the exact area that causes seizure activity. This will enable surgeons to target and remove only the epileptic foci, sparing healthy brain tissue.
Example: Intraoperative cortical stimulation can identify and preserve language areas during epilepsy surgery, reducing the risk of language deficits.
3.3. Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
DBS refers to the implantation of electrodes in certain areas of the brain to cure movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease. Brain mapping ensures the correct placement of electrodes for optimum therapeutic results.
Example: DTI can guide the placement of DBS electrodes, ensuring they target the correct neural pathways for symptom relief.
4. Advancements in Brain Mapping Technology
The continuous evolution of brain mapping is improving its accuracy and accessibility, thus becoming an integral part of neurosurgical practice with the development of new technologies.
4.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are integrated into the brain mapping technologies to efficiently analyze complex data sets. AI will be able to find patterns and predict outcomes that can help neurosurgeons make more informed decisions.
4.2. Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR)
These are immersive 3D models of the brain using VR and AR technologies to let surgeons visualize even the most intricate structures of the human brain and plan surgeries with unparalleled precision. These tools enhance both preoperative planning and intraoperative navigation.
4.3. Portable Brain Mapping Devices
New portable brain mapping devices are making it easier for neurosurgeons to access real-time data during surgery. These devices provide high-resolution images and real-time feedback, reducing the need for invasive procedures.
5. Benefits of Brain Mapping for Patients
Brain mapping offers numerous benefits for patients undergoing neurosurgical procedures. By providing detailed insights into the brain’s structure and functions, this technology enhances the safety and efficacy of surgeries.
5.1. Reduced Surgical Risks
It reduces the complication risks of motor, sensory, and cognitive deficits by exactly locating and saving important brain areas.
5.2. Improved Recovery and Outcome
Many patients undergoing surgery with the guidance of brain mapping experience quicker recoveries and have better long-term outcomes. This is because the preservation of important brain functions equates to a good quality of life after surgery.
5.3. Personalized Treatment Plans
Brain mapping thus allows for more personalized treatment because neurosurgeons can adopt strategies based on the unique brain anatomy and functional organization of each individual patient.
6. Conclusion
Brain mapping has indeed become an indispensable modern tool in neurosurgery and allows neurosurgeons the very precision and exactitude with which to treat gray matter in the human brain. This technology amplifies safety and efficiency in neurosurgical procedures due to its high-performance imaging and feedback in real-time, ensuring superior patient outcomes.
As technology continues to evolve, brain mapping will no doubt play an even greater role in the future of neurosurgery, offering hope for safer, more effective treatments and a brighter future for patients facing complex neurological conditions.
Also Read :
- Understanding Neuroplasticity: How Neurosurgery Can Aid Recovery
- How Neurosurgery Can Help with Peripheral Nerve Disorders
- How Neurosurgery Addresses Hydrocephalus in Adults and Children
- Spotlight on Spinal Cord Injuries: How Neurosurgery Can Help
- Neurosurgery for Pediatric Patients: Challenges and Triumphs