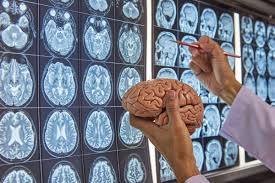
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into the field of neurosurgery is ushering in a new era of precision, efficiency, and improved patient care. As AI technologies rapidly evolve, they are being increasingly adopted across the medical field—particularly in complex disciplines like neurosurgery, where every millimeter counts. This article explores how AI is revolutionizing neurosurgery, the benefits it offers, and the challenges that still need to be addressed.
Artificial intelligence, encompassing machine learning, deep learning, and neural networks, is now being leveraged to analyze massive datasets, identify patterns, and support surgical decision-making. In neurosurgery, AI tools help in preoperative planning, intraoperative navigation, and postoperative monitoring. These tools enhance a surgeon’s ability to make informed decisions, reduce human error, and improve the overall outcome of surgeries.
Machine learning algorithms can analyze thousands of MRI and CT scans in seconds, detecting anomalies that may be overlooked by the human eye. Additionally, AI systems are trained on historical surgical data to predict potential complications, recommend optimal surgical pathways, and provide real-time feedback during procedures.
Precision and Accuracy: Key Benefits of AI in Neurosurgery
One of the most profound advantages of AI in neurosurgery is the remarkable improvement in surgical precision. By offering real-time 3D imaging and analysis, AI assists neurosurgeons in navigating the intricate anatomy of the brain and spinal cord with exceptional accuracy.
Preoperative Planning and Diagnosis
AI algorithms enhance diagnostic accuracy by interpreting medical imaging with high sensitivity and specificity. For instance, AI-based platforms can differentiate between tumor types, grade their severity, and identify their exact location and size. This enables surgeons to create tailored surgical plans that minimize tissue damage and preserve critical neurological functions.
Intraoperative Guidance
During surgery, AI-powered tools such as robotic surgical assistants and augmented reality overlays provide real-time updates and visualization. These tools track surgical instruments, map neural pathways, and warn surgeons if they are nearing sensitive regions of the brain. This level of intraoperative guidance minimizes risks such as hemorrhage or postoperative neurological deficits.
Postoperative Monitoring and Rehabilitation
AI doesn’t stop at the operating room. It plays a vital role in postoperative care by monitoring patient recovery through wearable devices and smart analytics. Predictive models assess the risk of complications like infections or seizures, allowing for timely interventions. Furthermore, AI is being used in neurorehabilitation through smart robots and virtual reality systems that assist in cognitive and physical therapy.
Enhanced Outcomes and Reduced Complications
The integration of AI in neurosurgery is leading to improved patient outcomes. By reducing human error and increasing the precision of interventions, patients experience fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
Studies have shown that AI-assisted neurosurgical procedures result in higher success rates in removing brain tumors and treating complex conditions like epilepsy or aneurysms. AI’s data-driven approach ensures that each step of the procedure is optimized for the best possible result, reducing the likelihood of reoperation.
The Role of Robotics in AI-Driven Neurosurgery
Robotic systems like ROSA (Robotic Stereotactic Assistance) and the da Vinci Surgical System are now integral parts of modern neurosurgical suites. These robotic platforms work hand-in-hand with AI software to enhance precision in minimally invasive surgeries. They reduce hand tremors, allow for smaller incisions, and improve dexterity in hard-to-reach areas of the brain.
Robotics and Automation: A Complement, Not a Replacement
It’s important to note that AI and robotics are designed to assist—not replace—neurosurgeons. While they offer unmatched precision and consistency, the intuition, creativity, and empathy of a human surgeon remain irreplaceable. The most effective outcomes are achieved when AI technology and human expertise work in harmony.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI-Assisted Neurosurgery
While the benefits of AI in neurosurgery are substantial, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure its safe and effective integration.
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems rely on vast amounts of patient data for training and decision-making. Ensuring the privacy and security of this sensitive information is paramount. Robust cybersecurity protocols must be implemented to prevent data breaches and maintain patient trust.
Bias in AI Algorithms
If AI algorithms are trained on biased or unrepresentative data, they may produce skewed results. This could lead to misdiagnosis or unequal treatment across different demographics. Continuous validation and updates are required to maintain fairness and accuracy in AI outputs.
Regulatory and Legal Concerns
The use of AI in surgical procedures raises questions about liability and accountability. If a complication arises due to an AI recommendation, determining responsibility can be complex. Regulatory frameworks need to evolve alongside the technology to ensure ethical and legal clarity.
Training and Adoption Barriers
Not all healthcare institutions are equipped with the infrastructure or expertise to implement AI systems. Training neurosurgeons and medical staff to work with these technologies requires time, investment, and curriculum redesign in medical education.
Future of AI in Neurosurgery: What’s Next?
As technology advances, the role of AI in neurosurgery will only continue to grow. Future developments are likely to include:
- Real-time Brain Mapping: AI algorithms that map brain activity in real time during surgery, offering unparalleled accuracy.
- Predictive Analytics for Personalized Treatment: Using AI to tailor surgical and therapeutic approaches based on individual genetic and physiological profiles.
- Autonomous Surgical Assistance: While full automation is still a distant goal, AI may one day perform certain routine tasks under supervision, increasing surgical efficiency.
The ongoing collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and medical professionals is key to unlocking these innovations. By fostering interdisciplinary research, the medical community can ensure that AI tools are safe, effective, and truly transformative.
Conclusion: The AI Advantage in Neurosurgery
AI-assisted neurosurgery is more than a technological trend—it’s a groundbreaking shift that is redefining how brain and spinal surgeries are performed. With improved precision, reduced risk, and better patient outcomes, AI is proving to be an indispensable ally in the operating room.
Despite the hurdles, the integration of AI into neurosurgical practice holds immense promise. As the technology matures, it will enable neurosurgeons to push the boundaries of what is possible, delivering safer and more effective care to patients worldwide.
Keywords: AI in neurosurgery, artificial intelligence surgery, robotic neurosurgery, brain surgery technology, AI surgical precision, neurosurgical innovation, smart healthcare solutions.
Also Read :