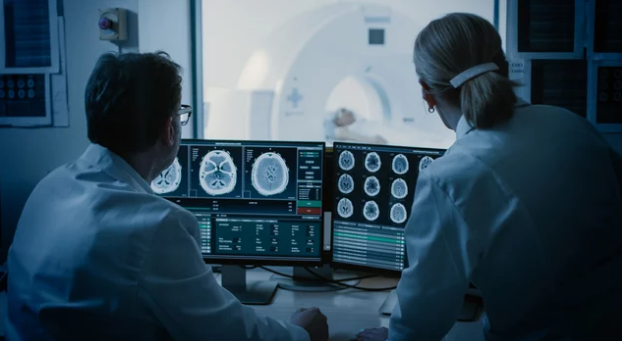
Medical education has always relied on visual learning. From cadaver dissections to illustrated textbooks, understanding anatomy depends on seeing the human body’s intricate structures in detail. However, with advancements in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and the rise of interactive visual tools, anatomy teaching has entered a new era—one where students can explore the human body in living, breathing, three-dimensional clarity without a scalpel in hand.
This approach not only enhances student engagement but also provides a more accurate, dynamic, and ethical learning experience compared to traditional methods.
The Shift from Traditional to Technology-Driven Anatomy Education
For centuries, cadaver dissection was the gold standard for teaching anatomy. While effective, it came with limitations—ethical concerns, high maintenance costs, limited availability, and the fact that cadavers represent static, lifeless tissue.
MRI technology, on the other hand, allows educators to present living anatomy—showing functional organs, blood flow, and even disease states in real patients. When paired with interactive visualization tools, this creates an immersive learning environment where students can:
- View anatomical structures in 3D.
- Explore cross-sectional slices of the body.
- Simulate real-time physiological processes.
- Learn through case-based clinical examples.
How MRI Enhances Anatomy Teaching
MRI offers unparalleled soft tissue contrast, making it ideal for visualizing complex anatomical details. In an educational setting, it enables:
1. Layer-by-Layer Exploration
Students can move through MRI slices to study structures layer by layer, mimicking the process of dissection but in a digital space.
2. Functional Anatomy Learning
Advanced MRI techniques, such as functional MRI (fMRI), allow students to see how different brain regions activate during specific tasks—bridging the gap between structure and function.
3. Disease Integration in Anatomy Lessons
Instead of learning anatomy in isolation, students can view normal and pathological structures side by side, improving diagnostic skills early on.
The Role of Interactive Visual Tools
When MRI data is combined with interactive anatomy platforms—such as 3D visualization software, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR)—the learning experience becomes truly engaging.
Key Features of Interactive Visual Tools for Anatomy Teaching
- 3D Reconstruction: Convert MRI slices into fully navigable 3D models.
- Clickable Structures: Label and describe organs, muscles, and vessels directly on the model.
- Cross-Sectional Matching: Compare MRI images with textbook diagrams for better comprehension.
- Zoom & Rotate: Examine structures from any angle.
- Integration with Clinical Cases: Link imaging to real patient histories for applied learning.
Benefits for Students and Educators
For Students
- Active Learning: Interacting with models increases retention.
- Self-Paced Study: Access MRI datasets anytime, anywhere.
- Better Clinical Preparedness: Exposure to real-world imaging builds diagnostic confidence.
For Educators
- Dynamic Teaching Materials: No need to rely solely on static slides.
- Adaptable Content: Lessons can be customized for different medical disciplines.
- Enhanced Engagement: Students are more likely to participate in discussions when visuals are interactive.
Real-World Applications in Medical Training
- Medical Schools: Replacing some cadaver dissections with MRI-based virtual labs.
- Radiology Training: Introducing students to image interpretation from the start.
- Surgical Education: Allowing surgeons-in-training to visualize anatomy relevant to specific procedures.
- Physiotherapy & Sports Medicine: Using MRI to teach musculoskeletal anatomy and injury mechanics.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits are clear, integrating MRI and interactive tools into anatomy education comes with challenges:
- High Costs: MRI scanning and visualization software can be expensive.
- Technical Skills Requirement: Both educators and students need training to use the tools effectively.
- Data Privacy Concerns: MRI scans of living patients require strict compliance with privacy regulations.
The Future of Anatomy Education with MRI
We are entering an era where mixed reality classrooms could become standard in medical education. In the near future, students may:
- Wear AR headsets to see MRI data overlaid onto a 3D anatomical model.
- Collaborate in virtual anatomy labs with peers worldwide.
- Access cloud-based MRI databases for self-directed study and research.
With advances in AI, smart systems could even personalize anatomy lessons based on a student’s progress, highlighting areas they struggle with most.
Conclusion
MRI and interactive visual tools are transforming anatomy education from a passive, observation-based process into an active, immersive experience. By offering a window into the living human body—in both health and disease—these technologies are preparing future healthcare professionals to think like clinicians from day one.
In the coming years, as accessibility improves and technology becomes more affordable, these tools will likely become a standard component of medical training worldwide.
If you want, I can now create SEO-optimized keywords, meta title, and description for this article so it’s ready to rank in the medical education and imaging niche.
Also Read :