Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Neurosurgical Procedures: How a Modality Improves Accuracy and Outcomes
DTI is one of the latest revolutions in the field of neurosurgery. It provides highly detailed pictures of tracts of white matter within the brain to help the neurosurgeon through a difficult structure during an operation. This type of imaging helps improve accuracy in surgical planning and sometimes greatly improves patient outcomes.
This would help the surgeons to understand connections of the brain more so that they may avoid certain specific parts while performing surgery. With DTI, the maintaining function while resecting tumors or other neurological problems improves. This is an important advancement in the minimal invasiveness procedures.
As DTI continues to evolve, even greater strides in neurosurgical applications can be expected. The level of understanding of its impact is important for those interested in brain surgery and the future and patients’ care.
Key Takeaways
- DTI provides accurate imaging of the brain anatomy for better planning of surgeries.
- The technology reduces risks during surgeries by marking off areas that need not be compromised.
- Further advances in the DTI will likely lead to better patient outcomes.
Basics of Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Diffusion tensor imaging is a form of advanced MRI technique. It provides detailed information about the white matter in the brain. This section covers the principles of DTI and its role in neurosurgical planning.
Principles of DTI
DTI measures the diffusivity of water in brain tissue, which is anisotropic; water can diffuse much more easily along the direction of the fiber tracts in white matter. This anisotropy can give important insights into the integrity of neural connections.
The main measures obtained by DTI are:
- Fractional Anisotropy: The extent to which there is directionality in water diffusion. The higher the FA, the healthier (or more intact) the white matter.
- Mean Diffusivity (MD): the average diffusivity of a voxel that can reflect tissue integrity. Tensor Model: A mathematical model indicating the characteristics of diffusivity in space. These allow for the visualization and interpretation of complex brain networks.
DTI in Neurosurgical Planning
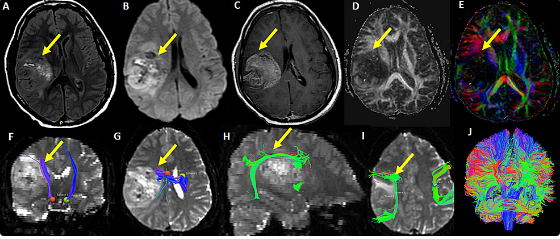
DTI plays an important role in neurosurgery for the demarcation of functional areas of the brain. It helps surgeons avoid vital pathways while carrying out surgery. The fine details of white matter tracts, provided by DTI, enable better surgical planning.
Applications of DTI in surgical planning include:
- Identifying Tracts: Knowledge of the location of motor and language pathways minimizes risk during surgeries.
- Preoperative Assessment: DTI is able to disclose changes in brain structure pre-operatively. This information shapes surgical approaches and techniques.
- Postoperative Monitoring: This helps in monitoring any changes in white matter integrity post-surgery.
Using DTI enhances the accuracy and safety of neurosurgical procedures.
Advances in Neurosurgery Due to DTI
Indeed, DTI has brought the desired change in neurosurgery. It allows for better preoperative planning, advanced surgical navigation, and even postoperative assessment, therefore making surgeries safer and effective.
Preoperative Assessment and Risk Mitigation
DTI will enhance the preoperative assessment by providing detailed pictures of the brain fibers. This enable the surgeon to identify critical areas like the corticospinal tract and language pathways. It helps in identifying the high-risk zones, thus preventing damage during the operation.
Using DTI data, surgeons are able to formulate personalized surgical plans. This, in turn minimizes complications. They will also be in a position to evaluate the chance of neurological deficits. This leads to well-informed consent discussions with the patients themselves.
Intraoperative Navigation and Real-Time Updates DTI allows intraoperative navigation tools to give the best real-time illustration of the tracts of the fiber in the brain during a surgical procedure. Such navigation tools guide surgeons towards tumor removal, avoiding important structures in the brain. The visual feedback makes sure the surgeons make better decisions on the fly.
Real-time DTI updates allow observation of changes in brain function during the procedure. That is an important capability because it allows the adjustment of the surgical approach if needed. It also expands the confidence and accuracy of the surgeon.
Postoperative Assessment and Patient Outcome
After surgery, DTI helps assess patient outcomes by demonstrating changes in brain fiber integrity. The extent of any damage made during the operation can be measured with accuracy. It enables surgeons to compare pre- and post-operative scans for better follow-up care.
Besides this, DTI gives information helpful in the prediction of the long-term recovery process. It may indicate how far healing and adjustment of the brain after surgery have gone. Such information goes a long way in rehabilitation planning in an overall perspective of patient care.
Also Read :