MRI and Image-Guided Neurosurgical Biopsies: Increasing the Accuracies of the Brain Diagnostic Workup The MRI is a majorstay in medicine today, particularly in neurosurgical intervention. MRI of the brain, therefore, allows the accurate targeting of tissue to be biopsied with the least insult to normal tissue. It revolutionized physicians’ ways of treating brain disorders, making interventions much safer and more successful.
It can identify exactly where abnormalities are located in the brain in image-guided biopsies. The ability to visualize structures in real-time is definitely important for successful outcomes. Of course, patients can therefore benefit from more accurate diagnoses due to such improvements, which may then lead to better treatment.
Currently, during these exciting times as neurosurgery continues to evolve, MRI-guided techniques stay one of the most current, impressively knitting together technology with patient care.
Key Takeaways
- MRI improves neurosurgical biopsy accuracy.
- Real-time imaging decreases procedural risk.
- Better Imaging means better diagnosis and treatment alternatives.
Fundamentals of MRI Technology
The principles of the technology behind MRI are very important in order to take images of the brain and other parts of the body in great detail. Understanding its basic principles, components, and safety considerations shall be handy in applying the device to the requirements of patients in a hospital.
Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI works through powerful magnets and radio waves, producing images of organs and tissues. As the person enters the MRI machine, the body’s hydrogen atoms align themselves with the direction of the magnetic field.
Radiofrequency pulses then knock them out of alignment. When the pulses are turned off, the atoms return to their natural alignment and emit energy. The energy is detected and, with computer processing, produces detailed images. MRI gives good contrast between soft tissues, hence it has a wide application in the diagnosis of many conditions.
Components of an MRI Machine
Basic Components of an MRI Machine:
- Magnet: The main constitutive part that supplies the excellent magnetic field; it might be open or closed.
- Gradient Coils: These coils enable the application of differential magnetic fields for better location of positions
- within the body. Radiofrequency Coils: These send and receive radio waves to capture detailed images. Computer System: It processes the signals from the coils to produce the final images.
These constituent elements, when put together, are able to allow the MRI to capture quality images for diagnosis and treatment planning.
Safety Concerns in MRI
MRI examination is associated with a number of safety concerns. A strong magnetic field may attract metal objects; therefore, patients have to be screened in caution.
Patients with implants such as pacemakers or even cochlear devices are not suitable for MRI scanning. There are also patients who need precautionary measures due to claustrophobia.
Technologists also take note of noise levels as the machine may be extremely loud. Ear protection may be provided to enhance comfort for the patient. Adequate preparation around the environment of the MRI ensures safety for the patient and operator.
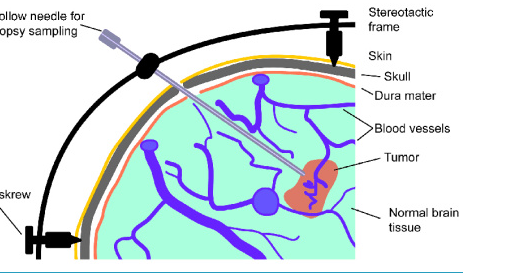
MRI-Guided Neurosurgical Biopsy Techniques
MRI-guided neurosurgical biopsy techniques are well planned and involve several accurate navigations. Such techniques allow surgeons to obtain tissue from brain lesions with minimal destruction of healthy tissue.
Preoperative Planning
Effective MRI-guided biopsy is planned preoperatively. A high-quality MRI scan is performed to locate and detail the site and nature of the lesion.
Scans are interpreted by surgeons with the use of software, whereby detailed mapping of the brain can be achieved. Surgeons may make use of techniques such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy to understand the composition of the tumor.
It also involves planning by counseling the patient about the procedure, risks, and benefits. This helps in planning about the most possible way of biopsy.
Intraoperative Imaging
Intraoperative imaging plays an important role in biopsy when using MRI guidance. This will help the surgeons in knowing the position of the biopsy needle during the operation through MRI images.
This form of imaging allows the adjustment of the needle to its correct position. This helps the surgeon in obtaining an appropriate sample from the lesion.
It also reduces the amount of time a patient must spend under anesthesia when utilizing intraoperative MRI. This can lessen complications and accelerate recovery for the patient.
Biopsy Needle Navigation
The process primarily involves the navigation of a biopsy needle. The surgeons navigate the needle with precision using special instruments collaborating with MRI technology.
They rely on a range of imaging pathways and robot systems to guide navigation. Such precision at retrieval of appropriate tissue samples is quite necessary.
Surgeons confirm the correctness of needle placement before biopsy could be taken. Navigation reduces the chances of damage to surrounding areas of the brain, hence improving patient outcomes.
Also Read :