Overview of MRI Imaging in Neurosurgical Treatment of Brain Metastases. MRI plays a central role in the neurosurgical treatment of brain metastases. By providing detailed pictures of the brain, MRI allows the physician to locate precisely the position and size of the tumor. This information is important in planning and then assessing the effectiveness of treatment.
For such patients with brain metastases, timely and accurate imaging often results in better outcomes. MRI not only helps follow the tumor activity but also provides information on the response to treatment. With increased usage, MRI enables more patients to receive personalized care, appropriate to their individual circumstances.
Understandably, this is by the explanation of how MRI imaging assists neurosurgical management, and hence one will understand its value in current medical practice. Such knowledge would thereby enlighten both the patients and their relatives as they go through various options in the management of their ailments.
Key Points
- MRI produces detailed pictures allowing identification and measurement of brain tumors.
- Accurate imaging improves treatment outcome by better planning and monitoring.
- Understanding the role of MRI ensures enhanced patient care and engagement.
Principles of MRI Imaging
MRI has been a helpful modality in understanding brain lesions. It utilizes large magnetic fields along with radio waves to generate high-resolution brain images. The generated images assist doctors in diagnosing the condition and deciding on further management of brain metastases.
Physical Principles: Basics of MRI
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. MRI makes use of the collaboration of a powerful magnet, radio waves, and a computer. When the patient is placed inside the machine, the magnet in the MRI generates an extremely powerful magnetic field that completely knocks the atoms in the body out of alignment, especially Hydrogen atoms, which are plentiful in water.
Once aligned, radio waves are passed through the body. These waves cause the aligned atoms to emit signals. The computer transforms these signals into a high-degree image. Different tissues in the brain send out different signals, while differentiation between normal and abnormal areas is clear.
Advancing MRI Technology
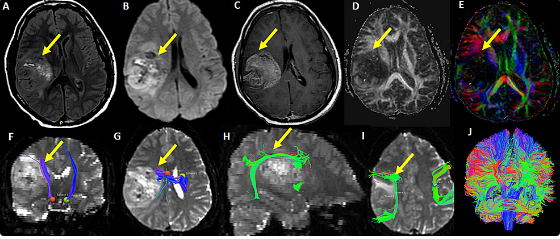
Recent development has significantly improved the technology of MRI. Newer machines provide high-resolution images where the identification of small lesions is quite easy. Functional MRI, or fMRI, helps in the study of the activity of the brain through the determination of changes in blood flow as a response to neural activity.
Techniques like DTI allow for better visualization of white matter tracts and thus help the surgeon to plan safer surgical routes around critical areas. Imaging techniques sometimes also involve the use of contrast agents, like gadolinium-based dyes, aimed at enhancing the clarity and detail in images, most especially in identifying tumors.
Safety of MRI and Patient Preparation
Safety first in MRI imaging: Before the scan, patients must eliminate from themselves all kinds of metal objects. They should avoid wearing jewelry, watches, or particular types of fasteners on their clothing. Even for people with metals implanted into their body, the strong magnetic field may be dangerous, such as a pacemaker or cochlear implant.
Proper patient preparation is necessary; this may include fasting or not drinking several hours before the test. The medical staff should be aware of the patient’s health conditions, medicines, or allergies. Comfort measures such as providing earplugs or a blanket will make the experience less unpleasant for the patient.
MRI Imaging in the Management of Brain Metastases
MRI thus plays a very important role in the diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases, helping the physician understand the extent of disease and appropriately plan the most suitable surgical intervention.
Role of MRI in Diagnosis
MRI is quite indispensable in the diagnosis of brain metastasis. It provides high-resolution images that are useful for clear visualization of brain structures. MRI is important in delineating tumors from normal brain.
It will reveal the lesions that may not be visible with the other imaging modalities. Since specific MRI sequences involve contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images, which are very useful in the delineation of tumor margins.
Key benefits:
- Lesion identification: MRI detects small metastases.
- Assessing the impact: It outlines the effect tumors have on the surrounding areas of the brain.
- Treatment planning: Accurate images guide clinical decisions accordingly.
Pre-Surgical Planning with MRI
Pre-surgical planning is useful in the effective treatment of patients. MRI provides comprehensive information about tumor size, location, and type. The modality helps the surgeon understand the tumor in relation to vital structures of the brain.
Key MRI Features in Planning: Tumor volume-the size will help in understanding what approach should be used. Location-MRI will illustrate if the tumor is near a vital structure, such as the motor cortex. Diffusion-weighted imaging will help in tumor cell density in some cases.
These can be useful in drawing up an efficient operation plan that may reduce a number of risks at surgery.
Intraoperative MRI Guidance
Intraoperative MRI is a modern tool that enhances surgical accuracy. Real time imaging within the operation theater is enabled to allow the surgeon to check on the state of the tumor.
The advantages intraoperative MRI possesses are as follows:
- Immediate feedback: Surgeons may inspect whether the tumor is completely taken off.
- Further actions may be done intraoperatively if residual tumors are detected based on adjustments made during surgery.
- This technology ensures that any residual tumor tissues are visualized and treated straight away for better results.
Post-Surgical Assessment
MRI is an important tool in the post-operative follow-up for assessing recovery after the surgery. MRI after surgery provides information on whether the complete tumor was taken out and also the complications that arise after the surgery.
Some key aspects of MRI in the post-surgical setting include:
- Detection of the Residual Tumor: It can indicate the presence of residual tumor tissue.
- Cerebral Changes: MRI can provide information about the changes taking place in the surroundings of the brain.
- Further management is guided by the results, which will indicate whether radiation or chemotherapy is necessary.
- Regular follow-up MRI is useful to observe the patient’s recovery and modification of treatment methods if necessary.
Also Read :