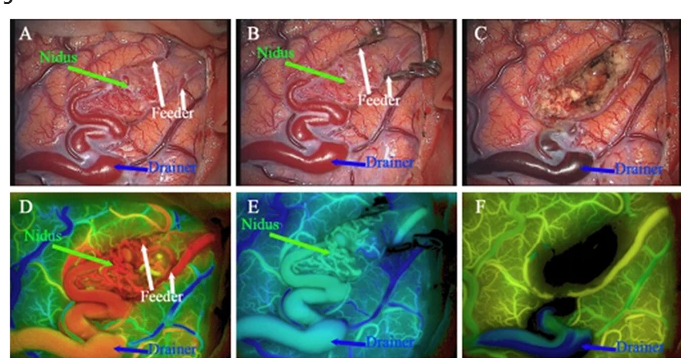
MR Angiography in Neurosurgical Management of Vascular Malformations: Techniques and Outcomes by Mr. Sachin L. Shah, FRCS, Scott C. Mitchell, Allen W. Barton, Gary B. Rajah, and Laligam N. Sekhar MR angiography is an important adjunct for neurosurgery in the management of vascular malformations. This advanced imaging methodology affords one of the most comprehensive examinations of blood vessels into the brain to assist in proper diagnosis and treatment. Of course, better understanding of its impact will go a long way in not only improving the outcomes in patients but also smoothening the surgical process.
These vascular malformations may present serious risks of bleeding or neurological deficits. MR angiography gives the surgeons crucial structural and functional information about the anomalies. Such information is useful in opting for the best course of action, which may range from surgery to mere follow-up.
As technology evolves, so does the use of MR angiography in further honing neurosurgical treatments. This approach better assesses complications, and treatments can be tailor-fit to the specific needs of the patient.
Key Takeaways
- MR Angiography provides detailed imaging of vascular malformations.
- It allows accurate diagnosis and treatment of neurosurgery.
- The technique improves outcomes by guiding surgical decisions.
Principles of MR Angiography
MR angiography is an important imaging modality that is used in the study and assessment of blood vessels within the body, but most importantly, the brain. It aids in the identification of vascular malformations and surgical planning.
Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Basically, MRI takes advantage of strong magnets and radio waves to achieve clear images of organs and tissues. In MR Angiography, blood vessels are the concern. MRI picks up the differences between the responses of blood and the tissues surrounding it when magnetic fields are applied.
Therein, two major principles come into play:
Magnetic Field: A strong magnetic field acts on the hydrogen atoms in the body, aligning them. These, after the turning of the field off, return to their prior positions, emitting signals.
Signal Processing: These are then processed, using special software, to produce highly detailed images of blood vessels. MR Angiography is far safer compared to other techniques such as X-rays, which make use of ionizing radiation.
Contrast Agents and Their Function
The contrast agents in MR Angiography enhance the visibility of blood vessels. These contrast agents possess elements that shift the magnetic properties of nearby water molecules.
Type of Contrast Agent:
- Gadolinium-based Agent: It is the most common type because it outlines the blood vessels very well. Gadolinium enhances those structures which could not have been well viewed.
- Safety Considerations: The majority of these agents are safe; however, some patients have been reported to develop adverse allergic responses and renal problems. Generally, renal function should be examined prior to the administration of contrast agents.
Contrast agents enhance image resolution tremendously, which is important for accurate diagnostics and treatment planning. The vascular malformations become more recognizable for the purpose of understanding their effects on the surrounding tissues.
Application in Vascular Malformations
MR angiography thus plays a significant role in vascular malformations management, from diagnosis through to the surgical treatment and follow-up process.
Diagnosis of Cerebral Aneurysms
MR angiography is useful in the diagnosis of cerebral aneurysms. The system provides excellent detailed views of the blood vessels in the brain. This non-invasive technique identifies the size and site of an aneurysm.
These results from MR angiography can be compared with other imaging techniques, such as CT, for confirmatory purposes. It also minimizes the chances of complications that may arise due to invasive procedures. The differential positioning of blood flow is beneficial for identifying potential avenues of treatment.
Pre-surgical Planning and Evaluation
Preoperatively, MR angiography gives the surgeon a perfect overview of the vascular anatomy. It defines the involvement of the vascular malformation with the underlying brain parenchyma.
It enables surgeons to plan the best approach possible by providing them with realistic images. MR angiography also demonstrates other vascular problems that may interfere with surgery. Clear visualization of blood vessels allows the surgical team to predict challenges and enhance safety in turn.
Follow-Up after Treatment
It is, therefore, an important modality for follow-up studies after treatment by MR angiography. The physician is able to observe the outcome of the interventions. They could determine if the treated malformation had been successfully treated or whether further action was required.
Early detection of vascular complications arising anew would be facilitated by appropriate imaging. In case these complications did set in, they could be managed in time. Such continued monitoring can thus result in an improved long-term outcome.
Also Read :