Integration of MRI and Robotics in Neurosurgical Procedures: Improving Precision and Safety in Surgery
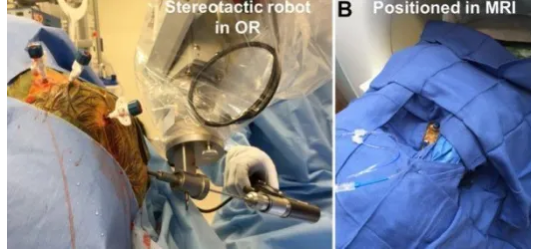
Neurosurgery has become increasingly sophisticated with time due to the incorporation of MRI and robotics into the operating room. Such a combination contributes to conducting surgery with greater precision and safety. The robotic systems guided by MRI allow surgeons to view real-time images of the brain while performing their surgical work, thereby contributing to the improvement in outcomes and reduction of risks.
With the increase in technology, the techniques used for surgeries also increase. Robots assist during such delicate procedures; they help give stability and reduce fatigue for the surgeon. The use of MRI gives surgeons critical information to move around the complex structures within the brain.
Understanding how MRI and robotics work together can change neurosurgical practices. As such advancements continue to develop and evolve, patients can benefit by having shorter recovery times and better overall care.
Key Takeaways
- MRI makes brain surgeries more accurate.
- Robotic machinery lessens the incidence of human error in procedures.
- Patients recover better because of this technology.
Principles of MRI-Guided Robotic Neurosurgery
MRI-guided robotic neurosurgery employs special imaging methodologies in conjunction with robotic systems to enhance the accuracy of brain surgeries. The concept has gone through numerous modifications in order to yield better results and make the procedures safer.
History of MRI in Neurosurgery
Neurological use of MRI began in the 1980s. Initially, it provided crucial images regarding diagnosis but did not integrate into surgical methodology. With time, there came a phase of development in MRI technology, which produced high-resolution images with the potential to visualize in real time during the procedure.
New imaging technologies, such as functional MRI, allow for more precise localization of regions of the brain responsible for movement, speech, and memory. The ability to do this enables surgeons to plan their procedures more effectively and to minimize injury to key tissues, which in turn makes the surgeries safer, and patients recover better.
Robotic Systems: Overview of Surgical Applications
Surgical robots possess a high degree of precision and flexibility during surgery. They further enable surgeons to make delicate, precise movements that may be hard to achieve with standard tools. A good example is the da Vinci Surgical System, where surgeons rely on robotic arms in performing most procedures.
The neurosurgical robots provide great help in targeting the lesion or tumor. Many systems have special tools to allow suturing, cutting, and other functions through complex brain structures. Surgeons may achieve heightened stability and a reduction in tremors to enhance overall accuracy in delicate procedures.
Advantages of MRI-Robotics Integration
The integration of MRI and robotics brings numerous advantages into neurosurgery. Real-time MRI imaging provides a vision of the brain during operations for the surgeon. This increases the accuracy of an intervention many times, especially targeted, with fewer complications.
Moreover, MRI will be able to monitor changes during the surgery itself, given immediate feedback. It enhances the ability to avoid critical areas in the brain, reducing risks.
The use of robotic systems combined with MRI also reduces the size of the incision. Smaller incisions result in less trauma, faster healing, and shorter hospitalization time. Such a combination thus results in increased safety and efficiency of the patients during neurosurgical procedures.
Clinical Applications and Techniques
The introduction of MRI with robotics has revolutionized neurosurgery. The combination of these modalities advances neurosurgical procedures by enhancing preoperative planning, intraoperative navigation, and postoperative assessment.
Preoperative Planning and Simulation
Preoperative planning also involves the use of MRI in order to get a clear, detailed picture of the brain. It is performed to outline tumors or other abnormalities and their size and location.
The robotic systems can simulate the surgery by allowing surgeons to go through mock attempts at the surgery. Such simulations are useful in predicting complications that may arise during the surgery and work toward improvement of surgery techniques.
Multidisciplinary teams may review and discuss data and strategies that could reduce risks associated with the surgery and therefore improve outcomes.
Intraoperative Navigation and Decision
Real-time MRI during surgery can provide the surgeon with correct information on the position of tissues. Thus, surgeons are assisted in intraoperative navigation to the targeted area with less injury to healthy tissues.
Imaging-integrated robotic systems enable finer accuracy in the positioning of surgical instruments. They can make adjustments in real time using this MRI guidance, increasing their safety.
In addition, better visualization enables surgeons to make proper decisions as quickly as possible. This speeds up the process during the operation and limits risk to the patients.
Assessment and Follow-Up after Surgery
- MRI is very crucial in postoperative assessment. It visualizes immediately the site postoperatively to check for any complication.
- Robotic tools can help even during follow-up. They monitor the recovery and ensure timely intervention if required.
Repeated assessment with MRI provides useful information that might lead to further modifications of the treatments themselves and improvements in patient care strategies.
Also Read :