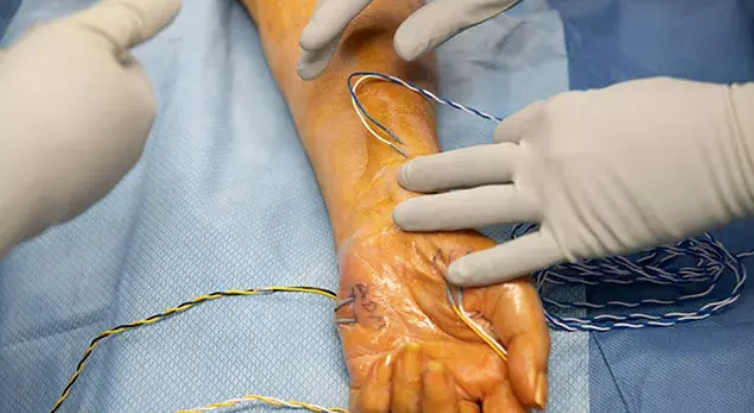
How Neurosurgery Can Help with Peripheral Nerve Disorders
Peripheral nerve disorders are debilitating and cause chronic pain, numbness, weakness, and impairment in mobility. These conditions arise when the peripheral nerves-the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord-are damaged or defective. Peripheral nerve disorders may arise from various factors, including injury, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, infections, and tumors.
Neurosurgery remains an important method of management and treatment of most peripheral nerve disorders, particularly in those instances where medical treatments, physical therapy, or changes in lifestyle are ineffective. This article intends to review the role neurosurgery plays in symptomatic alleviation, the restoration of function, and improvement in quality of life of patients with various peripheral nerve disorders.
1. Understanding Peripheral Nerve Disorders
Before the role of neurosurgery will be delved into, there should be an understanding of what peripheral nerve disorders are, and also many conditions can present the disorder.
What Is a Peripheral Nerve?
The peripheral nerves form an integral part of the nervous system by connecting the brain and spinal cord with other parts of the body. They convey messages between the CNS and the skin, organs, muscles, and all sensory receptors. Generally, injured peripheral nerves and pinched ones result in several signs and symptoms. Some are summarized as follows:
Pain: The feelings may present themselves as sharp, burning, or stabbing, constant or episodically.
Numbness and Tingling: The absence of feeling or a sensation analogous to “pins and needles,” frequently in the hands, feet, or limbs. Weakness: There is a decrease in strength of the affected region, thus giving impairment of motor skills and motility. Impaired Coordination: Difficulty in maintaining balance or performing fine motor tasks. Causes of Peripheral Nerve Disorders: Several conditions affect the peripheral nerves and include the following conditions:
Diabetic Neuropathy: The complication of diabetes to the nerves that involves pain, numbness, and weakness.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: This is the compression of the median nerve in the wrist, which might cause pain and tingling in this area of the hand. Peripheral Neuropathy: A general term for nerve damage to the peripheral nervous system, it can be brought about by trauma, infections, toxins, genetic causes, and many other causes. Traumatic Injuries: Accidental nerve injuries, including those from fractures or surgeries, may result in long-term damage and dysfunction.
Tumors or Growths: Pain and neurological symptoms arise when benign or malignant tumors compress nerves. Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions such as Guillain-Barré syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis result in inflammation and damage to peripheral nerves. While some peripheral nerve disorders are treatable with non-surgical means, others require surgical intervention to regain function and relieve symptoms.
2. When Does Neurosurgery Become Indicated for Peripheral Nerve Disorders?
Neurosurgery is usually considered when other treatment options-which include medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes-do not provide adequate relief. Surgery may be necessary in the following instances:
Severe Nerve Compression or Entrapment: Compression of nerves from surrounding tissues, such as muscles, bones, or ligaments, may cause pain, numbness, or weakness. In these cases, surgical decompression can relieve the pressure and restore nerve function.
Traumatic Nerve Injuries: When there is an injury, the peripheral nerves may be cut or damaged severely, thus requiring surgical repair or grafting of nerves. Persistence of Symptoms: If symptoms such as pain, weakness, or sensory loss persist, surgery may be indicated to prevent further deterioration of nerves and to improve the quality of life when all modes of conservative treatment have failed.
Nerve Tumors: Tumors or abnormal growths affecting peripheral nerves may require surgical removal to relieve symptoms and prevent further damage to the nerves.
3. Types of Neurosurgical Procedures for Peripheral Nerve Disorders
There are many types of neurosurgical procedures that can be used to treat disorders of peripheral nerves, depending on the nature and location of nerve damage. Some of the most common procedures include:
Nerve Decompression Surgery
Nerve compression is a condition wherein there is pressure exerted by surrounding tissues on the nerve, which disables its function and may cause pain, tingling, or weakness. Decompression surgery is used to relieve this pressure and restore normal nerve function.
Carpal Tunnel Release: One of the most common types of nerve decompression surgery is for carpal tunnel syndrome. In this procedure, the surgeon cuts the ligament that is pressing on the median nerve in the wrist, thus alleviating symptoms like hand numbness and tingling.
Radial Nerve Decompression: The radial nerve runs down the arm and can be compressed by injury or other conditions. Decompression can release the nerve and restore function.
Ulnar Nerve Decompression: Decompression surgery can take the pressure off of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, a condition called cubital tunnel syndrome, and may take some pressure off of the hand and fingers to decrease pain or weakness.
Peripheral Nerve Repair and Grafting
In cases of more severe damage and actual severing of a peripheral nerve, surgical repair of the nerve can be performed; this may take the form of nerve repair-the reconnection of the severed ends-or nerve grafting-sewing a portion of healthy nerve from another location in the body into the gap.
Nerve Repair: If the nerve has been cut, but the ends are still alive, the surgeon may try sewing the nerve ends together to restore function.
Nerve Grafting: If the ends of the nerve cannot be joined, then nerve grafting is performed. A small piece of healthy nerve is taken from another part of the body, often from the leg or forearm, and is used to connect the two damaged nerve ends.
Surgery to Transposition the Nerve
Transposition surgery may be indicated in cases where a nerve is entrapped or compressed by surrounding tissues. The surgeon moves the nerve to a different location where it will no longer be compressed, and the symptoms associated with it are relieved.
Transposition of the Femoral Nerve: There is compression of the femoral nerve in the hip, resulting in pain or weakness in the leg. Relocation of the nerve to another area relieves pressure and restores function. Sciatic Nerve Transposition: Patients who suffer from compression of the sciatic nerve have their nerves moved to a different position to avoid pain and the inability to move properly. Spinal Cord Stimulation (SCS)
For chronic peripheral nerve pain unresponsive to other treatments, spinal cord stimulation may be utilized. A small device implanted near the spinal cord delivers electrical pulses to disrupt pain signals and can ease conditions such as peripheral neuropathy or complex regional pain syndrome.
4. Benefits of Neurosurgery for Peripheral Nerve Disorders
Neurosurgery can significantly benefit patients with peripheral nerve disorders. Some of the important benefits of surgical intervention include:
Pain Relief:
Most neurosurgical procedures for peripheral nerve disorders aim at the alleviation of pain. Surgery significantly reduces or abolishes pain resulting from nerve compression or injury by nerve decompression, repair, or transposition.
Restoration of Function:
Most peripheral nerve conditions can cause a range of weaknesses or sensory losses that seriously impair a person’s ability to perform daily tasks. Surgery aimed at repairing or decompressing the affected nerve may help to restore motor function, improve strength, and increase capability in the performance of everyday activities.
Improved Quality of Life:
Chronic pain and disability from peripheral nerve disorders can detract from the quality of a patient’s life. Successful neurosurgical intervention can provide long-lasting relief, helping patients return to work, re-engage in social activities, and generally live more active, fulfilling lives.
Reduced Dependence on Medication:
Surgery can also reduce, or even totally eliminate, the need for pain medicines, including opioids, thereby minimizing the risks of dependence and adverse side effects. Patients whose symptoms are relieved following surgery on the nerve may no longer require any medicines to manage the symptoms.
5. Neurosurgery for Peripheral Nerve Disorders: Risks and Considerations
Like with other forms of surgery, neurosurgery for peripheral nerves also entails specific risks. Possible complications include:
Infection: With any kind of surgery, infection can be a complication that might make the process of recovery very distressing. Nerve Damage: While surgery is supposed to either repair or decompress nerves, there’s some small chance of nerve damage occurring during the surgery. Formation of Scar Tissue: This involves scar tissue around the nerve that could give rise to the symptoms again. Anesthesia Risks: As with any surgery, there are anesthesia risks, particularly for people with bad conditions.
Patients are highly encouraged to consult with their neurosurgeons concerning such risks and ensure they understand the expected benefits and difficulties of a proposed procedure.
6. Recovery and Rehabilitation after Surgery
Recovery and rehabilitation are extremely important parts of the healing process after neurosurgery for peripheral nerve disorders.
Tips for Recovery
- Rest and Recovery: The surgeon will direct the activities and rest that the patient must engage in during the several weeks after surgery.
- Physical Therapy: This may also involve physical therapy to regain strength, improve flexibility, and restore function to the affected area.
- Return to Normal Activities Gradually: Of course, recovery times will differ with different surgeries and individual healing; however, patients must ease back into their regular activities and not overexert themselves while recovering.
Conclusion
Neurosurgery also provides symptom relief to patients afflicted with chronic pain, weakness, or sensory loss due to peripheral nerve conditions. Neurosurgical interventions have been used for restoration of function and improvement in symptoms, and thus enhancement in the quality of life by decompression, repair, and stimulation techniques for nerve conditions. If you or your loved one has to live with a peripheral nerve disorder, it is best to seek consultation with a qualified neurosurgeon to discuss surgical options for your particular condition and take the first step toward a pain-free functional life.
Also Read :
- Exploring the Role of Neurosurgery in Combatting Chronic Pain
- The Link Between Neurosurgery and Restoring Mobility
- Innovative Technologies Transforming Neurosurgery Training
- The Impact of Neurosurgery on Treating Dementia-Related Conditions
- How Neurosurgery is Changing the Prognosis for Stroke Victims