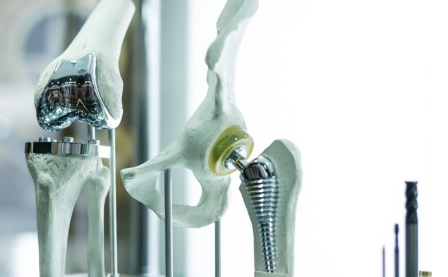
Titanium in Medicine: Transforming Healthcare with Biocompatible Materials
Introduction: The Silent Hero of Modern Medicine
In the rapidly advancing world of healthcare, materials science plays a pivotal role in developing solutions that enhance patient outcomes, extend lives, and improve quality of care. One element has quietly but powerfully revolutionized medical treatments—titanium. Celebrated for its strength, corrosion resistance, and most importantly, biocompatibility, titanium is transforming how doctors treat injuries, replace joints, and even repair damaged organs.
From dental implants to artificial hips and surgical tools, titanium is now a cornerstone in modern medical innovation. This article explores how titanium is shaping the future of healthcare and why it continues to be the metal of choice in life-saving technologies.
What Makes Titanium Ideal for Medical Use?
Titanium isn’t just a strong and durable metal—its biological compatibility makes it uniquely suited for medical applications. Let’s break down the key reasons:
- Biocompatibility: Titanium does not react adversely with the human body. It’s non-toxic, non-allergenic, and allows for osseointegration—the ability to bond directly with bone.
- Corrosion Resistance: Body fluids, which are highly corrosive, have no effect on titanium. It retains structural integrity for decades.
- Strength and Durability: Titanium matches steel in strength but is nearly 45% lighter, ideal for implants that need to last a lifetime.
- MRI Compatibility: Unlike some metals, titanium is non-ferromagnetic, making it safe for use in MRI environments.
- Hypoallergenic: Titanium is safe even for people with metal allergies, a common concern in orthopedic and dental applications.
Titanium in Orthopedics: Revolutionizing Joint Replacements
Joint Replacements and Implants
Titanium has become the gold standard in orthopedic surgery. Whether it’s a hip replacement, knee implant, or spinal fusion device, titanium-based components are favored for their durability and ability to integrate with bone.
- Hip and knee prosthetics: These are designed to last 20 years or more, thanks to titanium’s wear resistance and compatibility with surrounding tissue.
- Bone screws and plates: Titanium screws, rods, and plates are commonly used in trauma surgery to stabilize fractures and aid healing.
- Spinal implants: Titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio and non-interference with imaging scans make it ideal for spinal fusion surgeries.
Patients benefit from quicker recovery times, reduced inflammation, and long-term implant success.
Dental Implants: The Perfect Fit for Oral Health
Titanium has completely transformed the field of implant dentistry. Its unique ability to bond with bone through osseointegration ensures long-lasting, secure dental implants.
Why Titanium Works So Well in the Mouth:
- The jawbone readily integrates with titanium implants, providing a strong foundation for crowns or bridges.
- Titanium implants resist decay and do not corrode, even in the moist, acidic environment of the mouth.
- Patients often retain implants for decades with minimal maintenance.
As a result, titanium is the material of choice for over 95% of dental implant procedures worldwide.
Surgical Instruments: Precision with Strength
Titanium is also widely used in the production of surgical tools. These include:
- Scalpels and forceps
- Retractors
- Bone cutters
- Surgical scissors
Why surgeons prefer titanium instruments:
- They are lighter and easier to handle than steel tools, reducing surgeon fatigue.
- Titanium tools retain their sharpness longer.
- They are highly resistant to corrosion from sterilization processes.
In delicate procedures like neurosurgery or cardiovascular surgery, the precision and dependability of titanium instruments are invaluable.
Titanium in Cardiovascular Treatments
Titanium plays a vital role in the design and functionality of cardiovascular devices, such as:
- Pacemaker casings
- Artificial heart valves
- Stents
Its non-reactive nature ensures that it doesn’t trigger immune responses, making it safe for long-term implantation inside blood vessels or near the heart.
For patients with chronic heart conditions, titanium-based devices often mean the difference between life and death.
Advancements in 3D-Printed Titanium Implants
One of the most exciting developments in healthcare is the use of 3D printing with titanium powders to create custom implants. These patient-specific devices offer:
- Perfect anatomical fit
- Reduced surgery times
- Enhanced healing and comfort
Applications include:
- Facial reconstruction after trauma
- Customized joint replacements
- Cranial plates for neurosurgery
With 3D printing, the future of titanium in personalized medicine looks incredibly promising.
Titanium in Prosthetics: Enabling Mobility and Independence
Beyond internal implants, titanium is crucial in the development of prosthetic limbs. Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for:
- Lower and upper limb prostheses
- Sports prosthetics for athletes
- Advanced robotic limbs with sensors
Patients benefit from improved mobility, lighter devices, and longer-lasting prosthetics that enhance their day-to-day lives.
Biocompatible Coatings and Titanium Derivatives
Researchers are continually enhancing titanium’s properties by developing special coatings such as:
- Titanium nitride for increased hardness
- Hydroxyapatite coatings to enhance bone bonding
- Antibacterial surfaces to reduce infection risks
These innovations are helping medical professionals achieve better surgical outcomes, reduce complications, and extend the lifespan of implants.
Challenges and Considerations in Medical Titanium Use
Despite its advantages, the use of titanium in medicine presents some challenges:
- Cost: Titanium is more expensive than alternatives like stainless steel or certain polymers.
- Complex machining: Its strength makes it harder to shape and process, especially for intricate surgical tools.
- Allergy (rare): Though uncommon, a small percentage of patients may react to titanium, requiring alternative materials.
Nevertheless, these drawbacks are minimal when compared to the long-term benefits titanium provides in patient care.
The Future of Titanium in Healthcare
As healthcare becomes more personalized, data-driven, and technologically advanced, titanium will continue to play a crucial role. We can expect:
- Increased use of 3D-printed implants
- Nanotechnology-enhanced titanium surfaces
- Smart implants that interact with digital health monitoring systems
- Wider access to titanium-based care in developing regions through cost-effective production
The synergy between medical science and materials engineering ensures that titanium remains a pillar in the future of healthcare innovation.
Conclusion: A Titanium-Powered Healthcare Revolution
Titanium isn’t just a material—it’s a medical miracle. Its unique blend of strength, biocompatibility, and durability has revolutionized modern medicine. Whether it’s restoring a patient’s smile with a dental implant, enabling someone to walk again with a titanium hip, or saving a life with a pacemaker, titanium is quietly and powerfully improving millions of lives.
As technologies evolve and demand for safer, longer-lasting medical solutions increases, titanium will remain at the heart of healthcare innovation—reliable, resilient, and ready for the future.
Would you like this adapted for a medical website, blog post, or professional journal? I can tailor it to match any tone or audience.
Also Read :