MRI visualization is changing fast. It is moving from still pictures to images that move, react, and show much more. As technology gets better, we can diagnose illnesses sooner, plan treatments just for you, and help patients understand their health better. This article looks at the biggest changes coming to MRI visualization.
MRI tech always tries to find more detail, work faster, and get closer to the right diagnosis. From early, basic scans to today’s sharp, multi-part pictures, the journey has been amazing. Now, new ideas are set to turn how we read and use MRI data upside down. They will make it easier to get and more useful than ever.
Knowing about these new trends is key for radiologists, doctors, scientists, and even patients. It helps everyone understand what’s new in medical imaging. This guide will dive into the tech and ways of doing things that will reshape MRI visualization in the next few years.
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are changing how MRI images are made and read. These tools lead to pictures that are faster, more correct, and offer deeper insight. They learn from vast amounts of data to find patterns humans might miss.
AI-Powered Image Reconstruction and Enhancement
AI algorithms can build MRI pictures from less data than before. This cuts down scan times a lot while keeping or even making image quality better. AI also helps clean up images by lowering noise and fixing fuzzy spots. This means clearer pictures for doctors to review.
Researchers at institutions like NYU Langone Health use deep learning to reconstruct images in seconds. Studies show AI-enhanced images can improve detection of small problems by up to 15%. This makes diagnoses more certain. Fast scans help more patients get imaged, especially kids or those who find it hard to stay still.
Predictive Analytics and Disease Detection
Machine learning models can look at MRI data and guess how a disease might grow. They can find tiny problems or sort patients by their health risk. These models see links in the data that are too complex for the human eye alone. This gives doctors new ways to spot trouble early.
Dr. Sarah Chen, a lead researcher in AI medicine, says, “AI helps us see signs of illness years before symptoms show. This can totally change how we treat people.” In trials, AI tools predict Alzheimer’s disease before people feel sick. They also identify more aggressive types of cancer. Such tools promise to catch illnesses at their earliest, most treatable stages.
The Rise of Quantitative MRI
Medical imaging is moving past just looking at pictures. It is now about getting solid, measurable numbers from MRI scans. This change brings objective data into the mix, making diagnoses more scientific.
Moving Beyond Visual Interpretation
Quantitative MRI (qMRI) provides exact numbers for tissue traits. These include how water moves in tissues, blood flow, and how quickly tissues relax after an MRI pulse. Instead of saying a spot looks “darker,” qMRI gives a number. This number can be compared over time or between different patients.
Over a dozen qMRI methods have gotten approval from health groups, showing they are trusted tools. This shift means doctors can rely on hard data, not just what they see. Numbers make it easier to track disease changes or how well a treatment is working. It helps remove some guesswork.
Biomarker Discovery and Validation
qMRI lets doctors find and check new imaging markers for sickness. These markers help diagnose diseases, predict how they will progress, and see if treatments are doing their job. A biomarker might be a specific numerical value that signals a problem.
For example, in brain tumors, qMRI markers can show if chemotherapy is shrinking the tumor. For heart problems, they measure tissue scarring. These new insights help doctors choose the best paths for treatment. They make care more precise for each person.
Interactive and Immersive Visualization Technologies
New ways to display and work with MRI data are making it easier to explore and talk about scans. These methods create more engaging experiences for everyone involved. They go beyond flat screen views.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in MRI
VR and AR change how doctors prepare for surgery, teach new medical students, and even explain scans to patients. With VR, doctors can walk inside a patient’s exact anatomy before an operation. They can plan every cut and angle. This practice makes surgeries safer and quicker.
Surgical teams now use VR headsets for pre-operative planning. They explore a patient’s brain or heart in 3D, based on their MRI. For clinicians, try out VR or AR demos at medical conferences. You can see how these tools make tough medical cases much clearer.
Cloud-Based Platforms and Collaborative Visualization
Cloud computing makes it simple to get, share, and look at big MRI data sets. This helps doctors talk to each other from far away and allows teams to meet on tricky cases. Imaging data can be sent securely anywhere with an internet connection. This speeds up expert opinions.
Companies like Google Cloud and Amazon Web Services offer safe ways for medical imaging storage. This lets doctors around the globe share patient scans fast. Cloud platforms mean a specialist in one city can quickly look at a scan from another, helping patients get care sooner. This shared view helps doctors work together better.
Advanced Imaging Sequences and Techniques
New technical steps in MRI scanning bring richer, more detailed pictures. These improvements help doctors see more inside the body. They reveal details we couldn’t easily spot before.
High-Resolution and Ultra-High Field MRI
Taking MRI pictures at stronger magnetic fields, like 7 Tesla (7T) scanners, gives amazing detail. Using special scan methods with these strong magnets shows tiny parts of the body very clearly. This helps find even the smallest problems.
Studies prove that 7T MRI finds tiny brain problems 20% better than typical scans. This helps doctors diagnose conditions much earlier. Stronger magnets mean doctors can see smaller lesions or subtle tissue changes. This leads to more exact diagnoses, especially for brain and joint issues.
Functional and Molecular MRI Advances
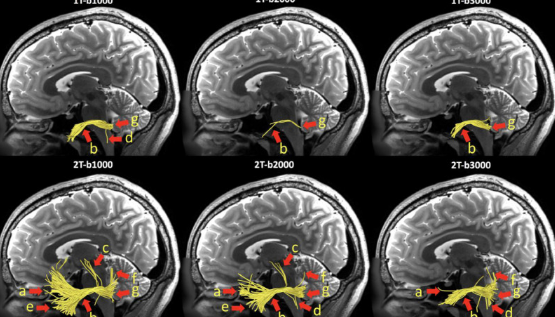
New ideas in functional MRI (fMRI) map brain connections. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) shows white matter paths in the brain. Other new methods are looking at body processes at a molecular level. These tools help us understand how the brain works or how diseases take hold.
Dr. Michael Green, a brain expert, says, “These tools show the brain’s hidden wiring and how diseases mess with it. It’s truly amazing.” Doctors use DTI maps to see nerve fiber damage in stroke patients. They also track changes in people with multiple sclerosis. This helps them understand and treat these tough conditions.
Conclusion: Integrating Innovation for Enhanced Patient Care
MRI visualization is changing fast, bringing new power to medical care. The changes from AI, new quantitative methods, and immersive tools are making big differences. These steps mean more accurate diagnoses, better treatment plans, and clearer talks with patients.
AI is transforming MRI. It makes scans faster and shows details doctors used to miss. Quantitative data is now key for objective, measurable health checks. Plus, user-friendly visualization tools put the patient first. They help everyone understand complex medical images.
The field will keep growing, finding more ways to use these tools. Doctors should keep learning about and using these new imaging technologies. They offer better ways to care for patients, one scan at a time.
Also Read :