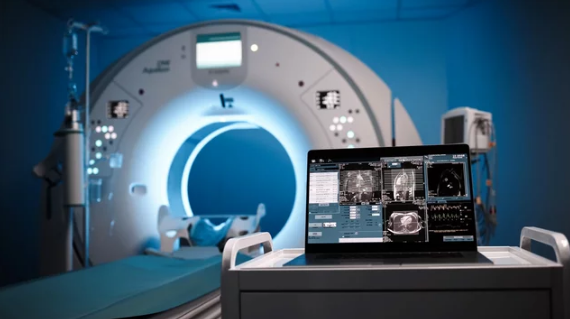
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has long been considered a cornerstone of modern medicine, delivering non-invasive insights into the human body with remarkable precision. However, the digital revolution has pushed MRI beyond simple imaging—it has transformed into a sophisticated visualization and diagnostic powerhouse. By combining advanced software, artificial intelligence (AI), and 3D rendering technologies, MRI now provides doctors and researchers with an unparalleled ability to interpret complex data, diagnose conditions earlier, and personalize patient care.
This article explores how MRI visualization has evolved in the digital era, why it is vital for healthcare, and how cutting-edge tools are shaping the future of medical diagnostics.
The Evolution of MRI in the Digital Age
When MRI technology first emerged in the late 20th century, it represented a groundbreaking leap from traditional X-rays and CT scans. Unlike other imaging methods, MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of internal organs, soft tissues, and the nervous system—without harmful radiation.
In the digital age, the technology has advanced in three crucial ways:
- Image Resolution: Modern MRI systems can capture ultra-high-definition images, making it possible to identify abnormalities at earlier stages.
- Visualization Software: Digital platforms allow radiologists to manipulate images in 2D, 3D, and even 4D, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
- Integration with AI: Algorithms can now detect subtle patterns that may escape the human eye, offering decision support for faster and more precise diagnoses.
The Role of MRI Visualization in Diagnostics
Visualization is more than just producing an image—it is about interpreting medical data in a way that empowers healthcare providers to make informed decisions. With modern visualization tools, MRI data can be reconstructed into detailed models that show anatomy, pathology, and even functional activity in real time.
Some of the diagnostic applications include:
- Neurological Disorders: Advanced MRI helps detect brain tumors, multiple sclerosis lesions, strokes, and early signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Cardiovascular Imaging: Visualization tools reconstruct the heart’s structure and blood flow, aiding in the diagnosis of congenital defects, blocked arteries, and heart muscle diseases.
- Orthopedic Conditions: 3D MRI allows surgeons to assess joint injuries, ligament tears, and cartilage damage with precision.
- Oncology: Tumor mapping using MRI visualization helps clinicians plan surgical interventions and monitor treatment progress.
3D and 4D MRI Visualization: Seeing Beyond the Surface
Traditional MRI produces flat, cross-sectional images. Today’s visualization platforms go much further.
- 3D MRI: Converts standard scans into lifelike models, enabling surgeons to “see” organs from any angle. This improves surgical planning and reduces risks during procedures.
- 4D MRI: Adds the element of time, capturing dynamic processes such as blood circulation, breathing, or joint movement. This is invaluable in understanding functional abnormalities.
For example, 4D cardiac MRI allows doctors to observe how blood flows through the heart chambers during each beat, leading to more accurate assessments of heart health.
Artificial Intelligence in MRI Visualization
AI-driven visualization is one of the most transformative innovations in modern diagnostics. Machine learning algorithms can rapidly process thousands of images, highlight potential problem areas, and even predict disease progression.
Key benefits of AI integration in MRI include:
- Faster Analysis: AI reduces reporting times by automatically classifying images and suggesting possible diagnoses.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Algorithms detect patterns that radiologists might miss, particularly in early disease stages.
- Personalized Medicine: AI tailors visualization to individual patients, making it easier to predict treatment outcomes.
Hospitals worldwide are adopting AI-assisted MRI software to streamline workflows, reduce human error, and improve patient outcomes.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in MRI Visualization
The digital age has also introduced immersive technologies such as VR and AR into MRI visualization. These tools take imaging to an entirely new level:
- Virtual Reality: Doctors and medical students can “step inside” 3D MRI scans, exploring anatomy in ways that textbooks and flat images cannot replicate.
- Augmented Reality: Surgeons can overlay MRI data directly onto a patient during operations, ensuring precision and minimizing risks.
This interactive visualization approach is not only transforming diagnostics but also revolutionizing medical training and patient education.
Cloud-Based MRI Platforms: Accessibility and Collaboration
One of the biggest challenges in medical imaging has always been the massive data storage requirements. Digital MRI visualization tools are now leveraging cloud computing to solve this issue.
- Remote Access: Specialists can access MRI scans from anywhere in the world, facilitating faster second opinions and telemedicine.
- Collaboration: Teams of doctors can simultaneously review scans, share annotations, and create treatment strategies in real time.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud storage reduces infrastructure costs for hospitals while ensuring secure and scalable data management.
By making MRI data more accessible, cloud-based platforms are breaking down geographical barriers in healthcare.
Benefits of MRI Visualization for Patients and Clinicians
The digital transformation of MRI offers wide-ranging benefits for both patients and healthcare providers:
- For Patients: Faster diagnoses, less invasive procedures, shorter hospital stays, and improved treatment outcomes.
- For Clinicians: Enhanced confidence in decision-making, reduced diagnostic errors, and improved efficiency in treatment planning.
Ultimately, advanced MRI visualization is making medicine more accurate, personalized, and patient-centered.
Challenges and Future Directions
While MRI in the digital age is revolutionary, challenges remain:
- High Costs: Advanced imaging systems and visualization software are expensive, limiting accessibility in low-resource settings.
- Data Security: Cloud-based storage and sharing raise concerns about patient privacy and cybersecurity.
- Training Needs: Radiologists and clinicians must continually update their skills to use new visualization tools effectively.
Looking forward, we can expect further integration of AI, quantum computing, and next-generation imaging sensors to push MRI capabilities even further. In the near future, fully automated, real-time diagnostic MRI systems may become the standard in hospitals worldwide.
Conclusion: MRI as a Digital Diagnostic Powerhouse
MRI in the digital age is no longer just about taking pictures—it is about visualization, analysis, and precision medicine. From 3D and 4D imaging to AI-driven analysis and immersive technologies like VR and AR, MRI is reshaping the way diseases are diagnosed and treated.
As healthcare becomes increasingly digital, MRI visualization stands at the forefront, bridging the gap between raw medical data and actionable insights. Its role as a diagnostic tool continues to expand, offering hope for earlier detection, better treatment outcomes, and a more patient-centered future in medicine.
Also Read :