MRI Techniques in Neurosurgical Evaluation of Cerebral Edema: Advancement and Applications MRI plays an important role in the assessment of cerebral edema, a factor that might bring about important changes in the patient’s outcome in neurosurgery. Advanced MRI techniques can help quantify the edema more precisely and monitor its progression or resolution, hence guiding better therapeutic decisions. The principle of functioning behind these advanced MRI techniques is necessary from a clinical standpoint for professionals who are into the practice of brain injuries or surgeries.
Cerebral edema has the potential to complicate surgical procedures; hence, precise imaging is important. MRI gives highly detailed pictures of the brain and helps the doctor view changes in the level of fluids and swelling of tissues. It also provides information about the nature of the patient’s pathology and helps in planning surgical procedures and monitoring treatments over time.
Thus, combining MRI techniques with neurosurgical assessment benefits the quality of patient care. This article discusses the importance of some MRI techniques and their direct effects on the management of cerebral edema, which the readers will learn about.
Key Takeaways
- MRI is an essential modality in diagnosing cerebral edema for neurosurgery.
- Advanced techniques yield clear images to help plan the treatment more effectively.
- Understanding such techniques means improving patient outcomes.
Basic Principles of MRI Techniques
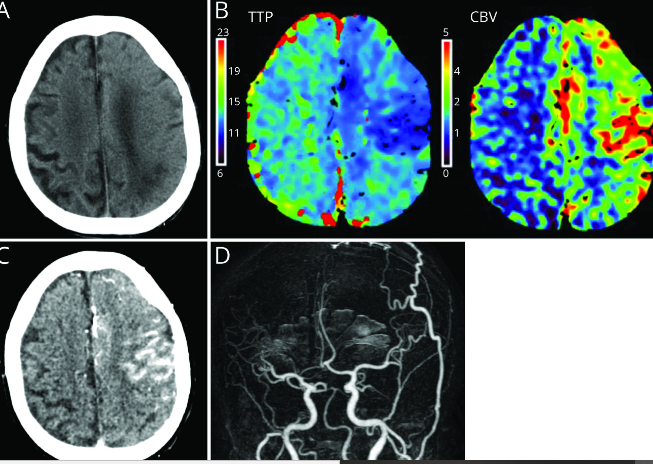
MRI represents an important modality in the evaluation of cerebral oedema. MRI images, detailed in the brain, are produced by using magnetic fields and radio waves. The simple basics of the principles that lay the foundation for the modality, sequence types, and the use of contrast agents facilitate effective evaluation.
Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI works on the simple principle of alignment of hydrogen atoms in the body with the help of a magnetic field. As radio waves are transmitted, the atoms send back signals. The machine detects the signals transmitted and converts them into images with the use of a computer.
The essentials involved in MRI:
- Magnetic Field: The strength of the magnetic field is measured in Tesla. The higher the Tesla value, the clearer the images will be.
- These protons can be excited, though, by radiofrequency pulses and cause them to resonate and, consequently emit signals.
- Images can delineate tissues, which again is critical for delineating oedema. Oedema appears as areas of increased signal intensity on MRI scans.
Types of MRI Sequences
There are many MRI sequences available that help in the delineation of various brain structures. Most of the commonly employed sequences include:
- T1-weighted images: Useful for assessment of anatomy and hemorrhages
- T2-weighted images: Very good for the evaluation of oedema and other lesions.
- FLAIR: It suppresses the signal of cerebrospinal fluid, which lets the subtle edema become more visible.
- Each one of these sequences provides different information; hence, they are useful in the diagnosis and follow-up of cerebral edema.
Contrast Agents in Cerebral Edema
- Contrast agents enhance the visibility of MRI images by increasing the contrast of certain structures. The ones used most often are gadolinium-based agents.
- These agents would help in depicting the following in the case of cerebral edema:
- Areas of breakdown in the blood-brain barrier
Increased vascularity with edema.
In acute edema, the contrast can outline abnormal patterns which may be very informative for treatment. It is essential, therefore, to know when and how to use these enhancing agents for proper diagnosis.
Application in Neurosurgical Assessment
MRI studies play a vital role in assessing cerebral edema during neurosurgery. They are useful in determining the extent of edema, in planning surgeries, guiding intra-operatively as well as finally monitoring recovery.
Assessment of Cerebral Edema
MRI is sensitive to the cerebral edema, which is the swelling of the brain tissue secondary to several etiologies. Edema may be pointed out by various MRI sequences such as T2-weighted and FLAIR.
- T2-weighted images: These will help identify regions of the brain that may be involved. It shows high signal intensity in places with edema.
- FLAIR sequences: These enhance the detection of edema by suppressing the signals of surrounding fluids, which aids in the better delineation of edema from CSF.
Appreciation of site and severity of edema is essential regarding consideration of the treatment modality.
Preoperative Planning
In the preoperative stage, MRI aids surgeons in the surgical approach. It gives clear pictures that help in the identification of anatomy of the brain and the extent of oedema.
Salient features include:
Identification of the critical structure: MRI shows the exact location of language centers or motor pathways.
The mass effect: The edema influence on surrounding brain tissue may help in surgical strategy; thus, a clear picture will enable surgeons to choose the best techniques and reduce risks.
Intraoperative Support
Real-time MRI during surgery can improve decision-making. Some techniques provide rapid imaging to enable the surgical team to confirm their approach and evaluate the state of the brain while operating.
Examples include:
- Intraoperative MRI Systems: These provide the surgeon with updated images of the brain, so that he is always informed about any changes in edema during the surgery.
- Navigational tools: MRI data can guide instruments with great accuracy, thus reducing the traumatization of healthy brain tissue.
This can lead to an immediate response that can be beneficial to the patients.
Follow-up After Surgery
MRI is also very crucial during postoperative follow-up following surgery. MRI helps in quickly identifying some of the complications like persistent or de novo edema among others.
The key factors that are monitored include:
- Edema decrease: The follow-up images can depict the reduction of the swelling.
- Complications: MRI depicts complications such as infection or hematoma that might require further intervention.
- This means that frequent MRI check-ups enable the timely amendment of treatment, hence leading to better patient care.
Also Read :