Advanced Imaging Technique and Outcomes in MRI for Neurosurgical Management of Trigeminal NeuralgiaTrigeminal neuralgia is a painful disorder that involves severe pain in the face. Due to trigeminal neuralgia, many seek effective treatment in order to solve such symptoms. The diagnosis and planning of neurosurgical intervention for this painful disorder are achieved through MRI technology.
Knowing how MRI can help in finding the reason for trigeminal neuralgia is important, as it can locate any pressure from the blood vessels or tumors which may impinge upon the trigeminal nerve. This information shall be very helpful for neurosurgeons to take further action on behalf of their patients.
While medical science is getting advanced, so is the usage of MRI in treating trigeminal neuralgia. Clear images provided are important for surgical decisions that improve patient outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- MRI helps outline the causes of trigeminal neuralgia.
- It assists the neurosurgical treatment plans effectively.
- Improvement in MRI helps further to improve patient care and outcomes.
MRI Technology in Trigeminal Neuralgia
MRI has become an imperative technology in the diagnosis and management of trigeminal neuralgia. It provides high-resolution images of brain structures, thus guiding surgical decisions. In the treatment of the condition, it would be important to understand the basic principles of MRI imaging, the role of MRI in assessment prior to surgery, and MRI navigational techniques.
Basic Principles of MRI Imaging
Imaging internal structures of the body is done by magnetic resonance imaging with the use of powerful magnets and radio waves. This is done without using radiation; hence, it is considered safer for the patients.
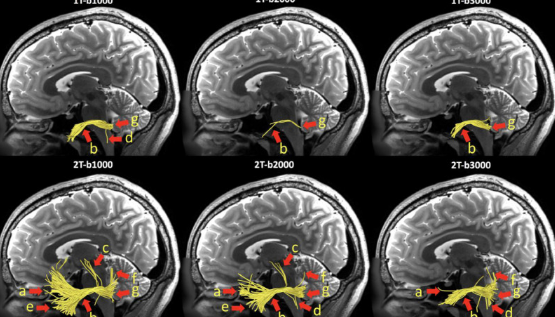
In the case of trigeminal neuralgia, MRI focuses on the brainstem and the pathways the trigeminal nerves course through. These imagings depict compressions, lesions, or any abnormality that could cause neuralgia.
The most commons MRI sequences are the T1 and T2-weighted images. Such types of a sequence provide good visualization of neural structure and its surrounding tissues.
Pre-Surgical Evaluation
The MRI plays a major role in pre-surgery evaluation of a patient. This is through assisting in the identification of the exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia, such as compression of a blood vessel on the trigeminal nerve.
Specific findings from MRI studies may dictate the choice of various surgical procedures, including microvascular decompression or rhizotomy. Physicians review the taken images to decide about a particular approach toward the surgery.
Interpretation of MRI findings gives physicians an idea of what can be expected from the surgery. Since they are using correct imaging, they enhance the possibility of alleviating pain or eliminating it for the patients.
Guide Navigation MRI in Procedures
Navigation MRI’s are high-tech technologies to add more accuracy to surgeries. It integrates real-time imaging and surgical planning together that guides neurosurgeons during their operations.
This technology enables surgeons to visualize the subtle anatomy of the brain when operating. It minimizes the possibility of damaging the healthy parts of the brain.
This navigation MRI will be able to locate the exact position of the trigeminal nerve. With such precise localization, the rate of success for surgeries involved in trigeminal neuralgia could be elevated to provide better results for the patients.
Clinical Applications
MRI plays a very important role in the management of trigeminal neuralgia. This is in regard to a better understanding of the pathophysiology and planning of treatment. Areas to be discussed in the application of MRI with emphasis will include:
Assessment of Neurovascular Conflict
A neurovascular conflict has been described as any location at which a blood vessel is in contact with the trigeminal nerve. Until today, a physical contact of a vessel with the trigeminal nerve may lead to pain in patients suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. This relationship can be adequately appreciated with the high-resolution imaging provided by MRI studies.
Physicians look for evidence of blood vessels impinging on the nerve. Images can demonstrate exactly the location of the blood vessel in relation to the nerve. This is important in planning surgery or other intervention.
Detection of neurovascular conflict informs decisions about management. It is a way that health care providers can assess the likelihood that surgery will alleviate pressure on the nerve.
Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Assessment
Other causes may be multiple sclerosis. MRI is important in the diagnosis of lesions within the brain and the spine. These lesions will give evidence to MS.
The MRI scans would show a difference in the brain tissue that would distinguish the MS from the other causes of trigeminal neuralgia. Identification of multiple sclerosis is of importance in treatment because the mode of treatment might differ from that of treating primary trigeminal neuralgia.
This shall help formulate the appropriate treatment protocols, knowing whether there is the presence of MS or not. It aids the doctor in monitoring the course of the disease to know when therapies need adjustment.
Imaging after Surgery
In cases of surgery to treat trigeminal neuralgia, it is MRI that will assess results. It will check if surgery has relieved the pain, and there are no complications.
The changes may be at the site of surgery that includes nerve damage or incomplete decompression. Based on such interpretations of images, doctors make the necessary changes to treat appropriately.
Follow-up MRIs help follow the progress, over time, in a patient’s recovery. This is for purposes of management for long-term cases of the trigeminal neuralgia.
Also Read :