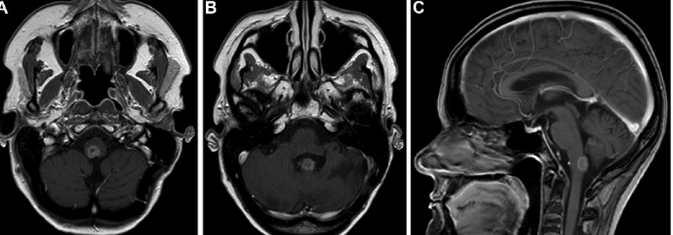
MRI-Guided Neurosurgical Interventions in Brainstem Lesions: Advances and Techniques The role of MRG has become very vital in the treatment of brainstem lesions. This innovative modality adds to the enhancement of precision, diminishes risks, and yields better patient outcomes. Real-time imaging is merged with actual surgical techniques that allow surgeons to perform navigation in more bewildering parts of the brain.
The brainstem is such a crucial part of the central nervous system, and many vital functions depend on it. Tumors and lesions are very difficult to operate due to their localization. MRI guidance gives better visibility to assure that all damaged tissue is dealt with while preserving healthy structures.
Advancement in technology continues to shape the future of neurosurgery. As techniques evolve, so does the hope that surgeries will be made safer and more efficient for the benefit of patients facing brainstem lesions.
Key Takeaways
- MRI guidance gives a superior level of precision with surgical resection of brainstem lesions.
- The most recent techniques reduce the intraoperative risk of complications.
- Improved imaging is coupled with better clinical outcomes in neurosurgical interventions.Basics of MRI-Guided
- NeurosurgeryIt brings together magnetic resonance imaging and surgical techniques for improved outcomes in brain surgeries. The key highlights of the topics that will be discussed in the review include principles of MRI imaging, state-of-the-art technological advancements, and integration with neuronavigation systems.
MRI Principles of Imaging
MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to produce clear images of the brain. This modality provides high resolution for soft tissues, thus making it suitable for the visualization of brainstem lesions. The MRI does not use ionizing radiation, unlike CT scans.
Imaging would also include the use of different types of sequences such as T1 and T2-weighted images that highlight various aspects of the tissues being imaged. Generally, T1-weighted images are used for anatomic detail while T2-weighted images are helpful in detecting oedema and abnormalities.
Tissue contrast may enable surgeons to delineate between normal and pathological tissues. MRI can also provide functional imaging of organs. This helps in identifying those areas which are responsible for speech, motor function, etc.
Technological Advances in MRI Systems
Recent development has phenomenally upgraded the technology of MRI. Newer MRI systems have stronger magnetic fields, yielding better image resolution and often shorter scanning time. It helps in capturing quicker images during surgery.
In addition, it has improved image processing owing to software improvements. In a presentation format, it enables better viewing of anatomic structures and lesions within the brain. Various tools like diffusion tensor imaging allow the surgeon to know about the anatomy of white matter tracts, thereby steering clear of critical tracts.
Apart from this, new methods like fMRI are being utilized to assess the activity of the brain while the subject is engaging in a particular task; the results have enhanced surgical planning. This, in return, has significantly facilitated the surgeons to make decisions which were more viable, hence minimizing risks associated with such procedures.
Neuronavigation Integration
The neuronavigation systems use MRI for their input data to track the position of the surgical tool accurately. This integration allows for real-time tracking during operations. The surgeon can see the patient’s anatomy on the screen and is thus more precise.
The software registers preoperative MRI images with the current anatomy of the patient. This helps in ascertaining the exact site of a lesion in the brainstem. The image is also updated as the surgical procedure proceeds.
Neuronavigation makes the surgery safer and more effective. It reduces the possibility of damaging healthy tissues during the process of surgery. With the advent of MRI along with neuronavigation, surgeries turned out to be pretty fast and efficient; this resulted in better patient outcomes.
Surgical Techniques for Brainstem Lesions
The surgical techniques of treating brainstem lesions are therefore done with the utmost care and require precision in their execution. Emphasis is on preoperative preparation, the use of intra-operative MRI, and proper assessment post-surgery.
Preoperative Planning
It is important to begin neurosurgery on brainstem lesions with preoperative planning. Very careful history and review of studies are carried out. MRI scans help the surgical team in identifying the size of the lesion, its location, and relation to important structures.
A multidisciplinary team collaborates in this phase. This involves neurosurgeons, radiologists, and anaesthesiologists. They will review the procedure for an idea of the potential risks involved and come up with strategies tailored to the particular case. They also provide the patient with information about the surgery, risks associated with it, and the anticipated recovery outcomes. Accurate planning enhances safety and effectiveness during surgery.
Intraoperative MRI
Among the modern developments, intraoperative MRI is one that significantly enhances the surgical precision of surgeons. This technology allows surgeons to capture appropriate images of brain structures at the time of surgery. They can assess the size of the lesion and whether it has been completely removed.
Surgeons are able to adjust their approach based on the real-time imaging findings. The immediate feedback enables them to keep as far as possible from the surrounding sensitive structures to minimize injury to nerves and vessels. Intraoperative MRI reduces the risk of complications and improves the chance of a favorable surgical result.
Postoperative Assessment
Assessment post-surgery is a crucial element in estimating the success of the surgery. Medical teams closely monitor complications and neurological deficits. Imaging studies are performed on a regular basis to evaluate the site of surgery.
The surgical team then evaluates the patient’s recovery process, whether it is good or poor. Early detection of complications is done for early intervention. Follow-up visits at regular intervals provide continuity for assessing the condition of the patient postsurgery. This forms a very integral part of achieving the best patient outcomes.
Also Read :
- Using MRI to Assess Neurosurgical Interventions for Chronic Pain
- MRI-Based Radiomics in Neurosurgical Outcome Prediction
- MRI Innovations in Neurosurgical Robotics and Navigation Systems
- MRI Techniques in Neurosurgical Evaluation of Cerebral Edema
- MRI Imaging in Neurosurgical Treatment of Brain Metastases